Chronic Kidney Disease, commonly referred to as CKD, is a progressive condition that affects the kidneys’ ability to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood. Over time, this can lead to a buildup of toxins in the body, causing a range of health complications. This article provides an in-depth look at Chronic Kidney Disease, including its causes, symptoms, and essential care strategies.
Understanding Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic Kidney Disease is a long-term condition characterized by the gradual loss of kidney function. The kidneys play a vital role in maintaining overall health by filtering waste products, balancing electrolytes, and regulating blood pressure. When these organs are damaged or unable to perform their functions effectively, it can lead to serious health issues.
The progression of Chronic Kidney Disease is typically slow and may not show noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the disease advances, it can result in severe complications such as cardiovascular disease, anemia, and bone disorders.
Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease
- Stage 1: Kidney damage with normal or high kidney function.
- Stage 2: Mild reduction in kidney function.
- Stage 3: Moderate reduction in kidney function.
- Stage 4: Severe reduction in kidney function.
- Stage 5: Complete kidney failure, often requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant.
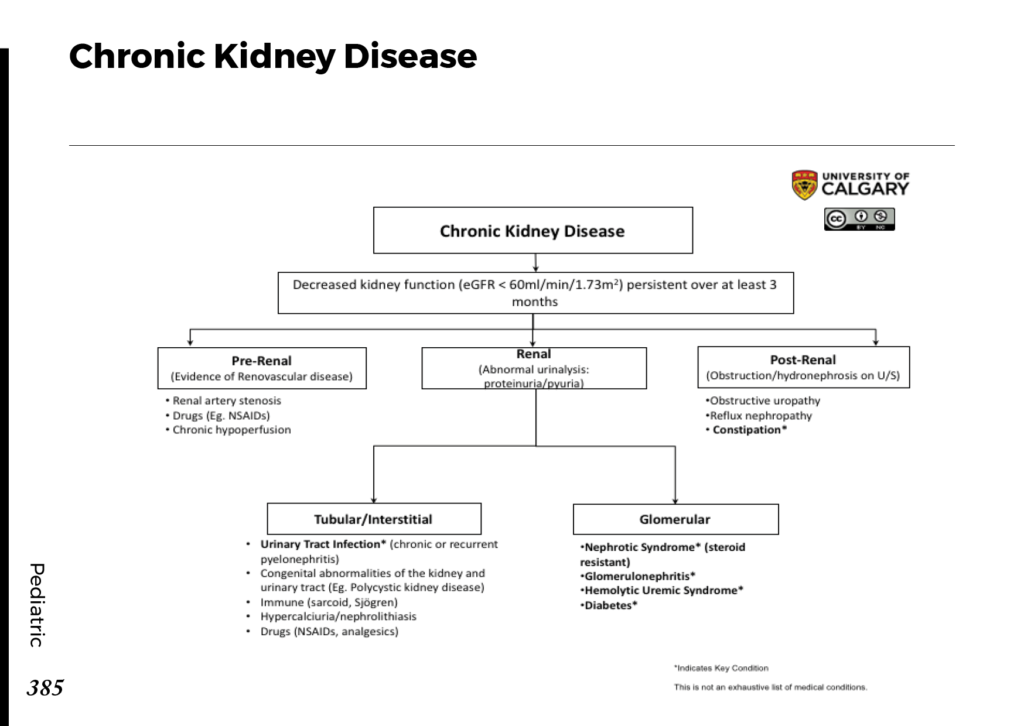
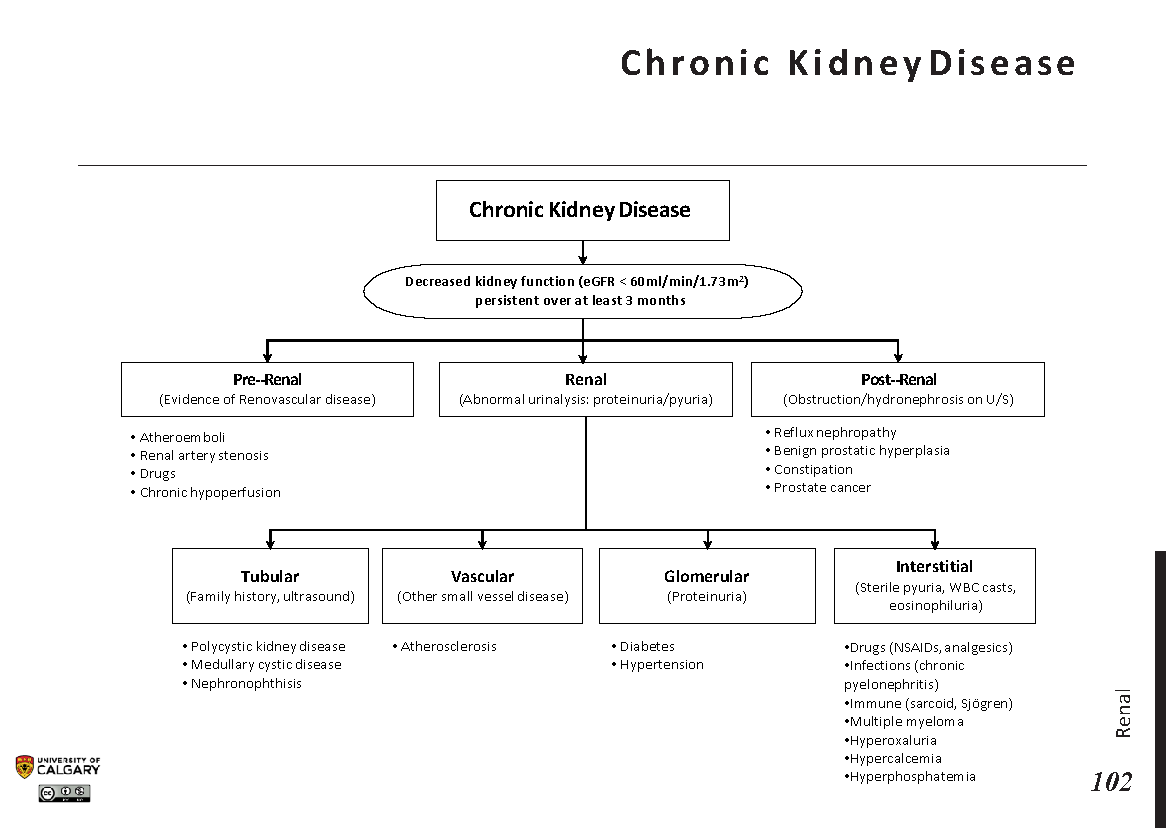
Causes of Chronic Kidney Disease
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of Chronic Kidney Disease. Understanding these causes is crucial for prevention and early detection.
Diabetes
Diabetes is one of the leading causes of Chronic Kidney Disease. High blood sugar levels over time can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their ability to filter waste effectively. Managing blood sugar levels is essential to reduce the risk of kidney damage.
Hypertension
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, can also cause significant damage to the kidneys. Elevated blood pressure puts extra strain on the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to scarring and reduced function. Controlling blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medication is critical in preventing further damage.
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis refers to inflammation of the glomeruli, which are tiny filters within the kidneys. This condition can be caused by infections, autoimmune diseases, or other underlying health issues. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent progression to Chronic Kidney Disease.
Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic Kidney Disease is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous cysts in the kidneys. These cysts can enlarge over time, leading to kidney damage and eventual failure. While there is no cure for this condition, treatments are available to manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
Other Causes
Other potential causes of Chronic Kidney Disease include prolonged use of certain medications, recurrent kidney infections, obstructions in the urinary tract, and autoimmune conditions like lupus. Identifying and addressing these underlying causes is key to managing the disease effectively.
Symptoms of Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic Kidney Disease often progresses silently, with symptoms becoming apparent only in the later stages. Recognizing these symptoms early can help individuals seek timely medical intervention.
Early Symptoms
- Fatigue and weakness
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Persistent itching
Advanced Symptoms
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Difficulty concentrating
- Muscle cramps and twitches
- Shortness of breath
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be associated with other health conditions. Therefore, consulting a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and evaluation is essential.
Caring for Chronic Kidney Disease
Managing Chronic Kidney Disease requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medical treatments, and regular monitoring. Here are some key strategies for effective care.
Dietary Adjustments
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in managing Chronic Kidney Disease. Individuals with this condition should focus on reducing their intake of sodium, potassium, and phosphorus. Foods high in these minerals can place additional strain on the kidneys and worsen the condition.
- Limit processed foods and fast food, which are often high in sodium.
- Choose fresh fruits and vegetables that are low in potassium.
- Avoid dairy products and processed meats that contain high levels of phosphorus.
Working with a registered dietitian can help create a personalized meal plan tailored to individual needs and preferences.
Medication Management
Medications are often prescribed to manage symptoms and slow the progression of Chronic Kidney Disease. Common medications include:
- Blood pressure medications to control hypertension.
- Diabetes medications to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Erythropoietin supplements to treat anemia.
- Vitamin D supplements to support bone health.
It is important to take medications as prescribed and attend regular check-ups to monitor their effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to dietary changes and medication, adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with Chronic Kidney Disease.
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, to maintain overall health.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as these can exacerbate kidney damage.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring is essential for individuals with Chronic Kidney Disease to track kidney function and detect any changes early. Routine tests may include blood tests to measure creatinine levels, urine tests to check for protein, and imaging studies to assess kidney structure.
Follow-up appointments with healthcare providers allow for ongoing evaluation and adjustment of treatment plans. Staying proactive in managing the condition can help prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Living with Chronic Kidney Disease
While Chronic Kidney Disease is a lifelong condition, many individuals can live fulfilling lives with proper care and management. Education and support are vital components of living well with this disease.
Support Networks
Connecting with others who have Chronic Kidney Disease can provide emotional support and practical advice. Support groups, both in-person and online, offer a platform for sharing experiences and learning from others facing similar challenges.
Educational Resources
Access to reliable information about Chronic Kidney Disease is essential for making informed decisions about care. Healthcare providers, reputable websites, and patient advocacy organizations can serve as valuable resources for learning more about the condition and available treatments.
Emotional Well-Being
Living with a chronic illness can take a toll on mental health. It is important to prioritize emotional well-being by seeking counseling or therapy if needed. Addressing feelings of anxiety or depression can improve overall quality of life and enhance coping skills.