Chilblains, also known as pernio, are a common yet often misunderstood condition that affects the skin, particularly during colder months. These small, itchy swellings on the skin occur as a result of an abnormal reaction to cold temperatures. While they are not life-threatening, chilblains can cause significant discomfort and may lead to complications if left untreated. In this article, we will explore what chilblains are, their causes, symptoms, and available treatments in detail.
What Are Chilblains?
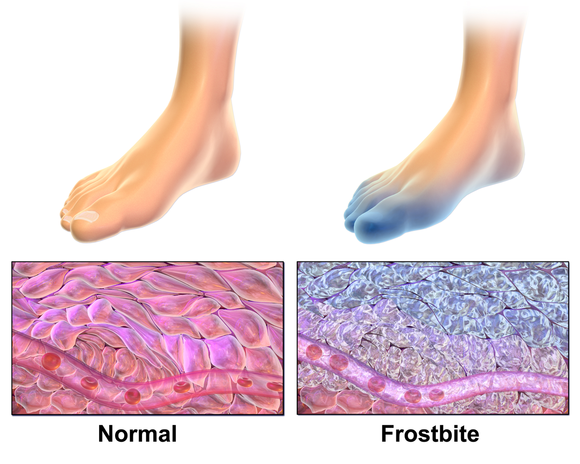
Chilblains are localized areas of inflammation that develop on the skin when exposed to cold but not freezing temperatures. They typically appear on extremities such as fingers, toes, ears, and nose, which are more prone to temperature changes. The condition arises due to the body’s response to rewarming after being exposed to cold conditions. When the skin is suddenly warmed up, the blood vessels near the surface expand too quickly, leading to leakage of fluid into nearby tissues and causing swelling, redness, and itching.
Who Is at Risk?
- Individuals who live in regions with damp and cold climates.
- People with poor circulation or underlying health conditions like Raynaud’s phenomenon.
- Women are more likely to develop chilblains than men.
- Children and elderly individuals are at higher risk due to their sensitive skin and slower circulation.
Causes of Chilblains
The exact cause of chilblains is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to their development:
Exposure to Cold Temperatures
Chilblains occur when the skin is exposed to cold temperatures for extended periods. Unlike frostbite, which happens in freezing conditions, chilblains develop in temperatures above freezing but below normal body temperature. This makes them more common in regions where winters are chilly but not severe.
Rapid Rewarming
One of the primary triggers for chilblains is the sudden warming of cold skin. For instance, placing cold hands directly under hot water or using a heater can cause blood vessels to expand rapidly, leading to inflammation and irritation.
Poor Circulation
People with poor blood circulation are more susceptible to developing chilblains. When blood flow is restricted, the body struggles to regulate temperature effectively, making the extremities more vulnerable to cold-induced damage.
Underlying Health Conditions
Certain medical conditions increase the likelihood of developing chilblains. These include:
- Raynaud’s phenomenon: A condition where blood vessels in the fingers and toes constrict excessively in response to cold or stress.
- Lupus: An autoimmune disease that affects various parts of the body, including the skin.
- Anemia: Low levels of red blood cells can impair oxygen delivery to tissues, exacerbating sensitivity to cold.
Symptoms of Chilblains
The symptoms of chilblains usually appear within hours of exposure to cold temperatures and can last for several weeks if untreated. Common signs include:
Red or Bluish Patches
Small, red patches or bluish discoloration may appear on the affected areas. These patches are often swollen and tender to touch.
Itching and Burning Sensation
One of the hallmark symptoms of chilblains is intense itching accompanied by a burning sensation. This discomfort tends to worsen as the skin warms up.
Blisters and Ulcers
In severe cases, chilblains can lead to the formation of blisters or even ulcers on the skin. These open sores increase the risk of infection and require prompt medical attention.
Swelling
Affected areas may become swollen, making movement difficult, especially if the toes or fingers are involved.
Treatments for Chilblains
While there is no specific cure for chilblains, several treatment options can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications:
Gradual Rewarming
If you suspect you have developed chilblains, avoid exposing the affected area to direct heat sources like radiators or hot water. Instead, gradually rewarm the skin by covering it with warm clothing or immersing it in lukewarm water (not hot). This approach minimizes the risk of aggravating the condition.
Topical Creams
Over-the-counter corticosteroid creams can reduce inflammation and relieve itching associated with chilblains. Applying these creams regularly as directed can provide significant relief.
Oral Medications
In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications such as calcium channel blockers to improve blood flow and reduce the frequency of chilblain episodes. Other oral treatments, like antihistamines, may be recommended to manage severe itching.
Preventive Measures
Prevention plays a crucial role in managing chilblains. Here are some tips to minimize your risk:
- Dress warmly in layers during cold weather, paying special attention to extremities like hands, feet, and ears.
- Avoid wearing tight shoes or gloves, as they can restrict blood flow.
- Keep your home adequately heated and use insulated footwear indoors if necessary.
- Exercise regularly to promote healthy circulation.
- Quit smoking, as nicotine constricts blood vessels and impairs circulation.
Natural Remedies
Some people find relief from chilblains through natural remedies. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider before trying any alternative treatments. Popular options include:
- Aloe vera gel: Known for its soothing properties, aloe vera can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Calendula ointment: This herbal remedy has anti-inflammatory effects and may aid in reducing redness and swelling.
- Ginger tea: Consuming ginger tea or applying ginger paste to the affected area can improve circulation and alleviate symptoms.
When to See a Doctor
Most cases of chilblains resolve on their own within two to three weeks. However, certain situations warrant professional medical advice:
- If the affected area becomes infected, characterized by pus, increased pain, or fever.
- When symptoms persist despite self-care measures or recur frequently.
- If you notice worsening discoloration or ulceration of the skin.
Your doctor may perform a physical examination and ask about your medical history to determine the best course of action. In rare cases, additional tests may be required to rule out underlying conditions contributing to the problem.
Living with Chilblains
Managing chilblains involves adopting lifestyle changes and being mindful of environmental factors. By understanding the causes and implementing preventive strategies, you can significantly reduce the impact of this condition on your daily life. Remember that early intervention and proper care are key to minimizing discomfort and preventing long-term complications.