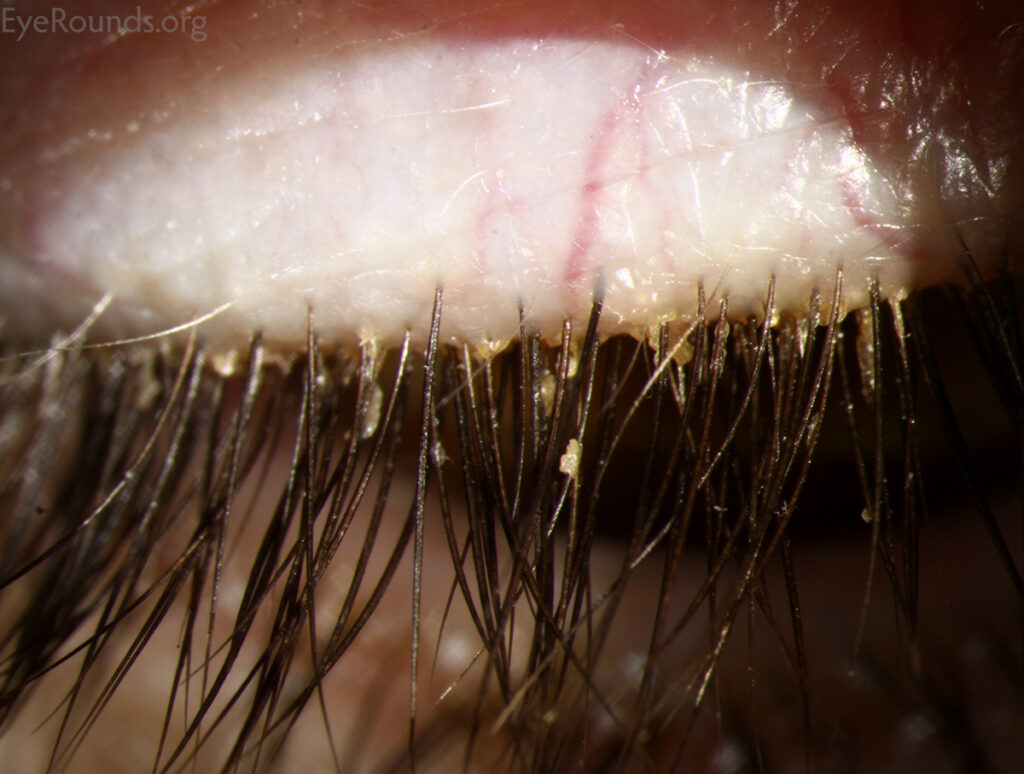
Blepharitis, often abbreviated as BE, is a common yet frequently misunderstood condition that affects the eyelids. It causes inflammation of the eyelid margins, leading to discomfort and potential complications if left untreated. This article explores the underlying causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for this condition in detail.
What Is Blepharitis?
Blepharitis refers to an inflammation of the edges of the eyelids, where the eyelashes grow. The condition can occur in people of all ages and may be chronic or acute. It is not contagious but can significantly impact daily life due to its persistent nature. There are two main types of blepharitis:
- Anterior blepharitis: Affects the outside front edge of the eyelids, near the base of the eyelashes.
- Posterior blepharitis: Involves the inner edge of the eyelids, which comes into contact with the eyeball.
Causes of Blepharitis
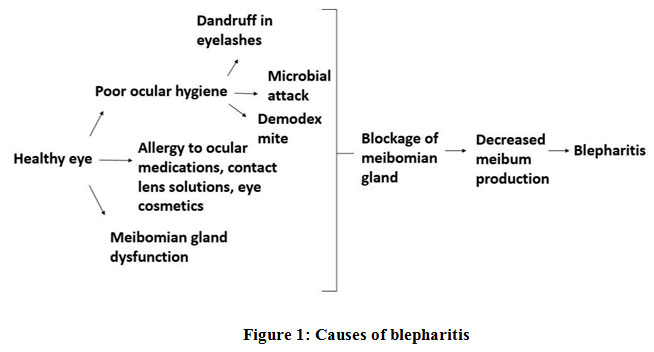
The exact cause of blepharitis can vary depending on the type and individual circumstances. However, several factors are commonly associated with its development:
Bacterial Infections
Bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus are often found in cases of anterior blepharitis. These bacteria thrive on the skin and can lead to infection when they accumulate around the base of the eyelashes. Poor hygiene practices, such as infrequent cleaning of the eyelids, can exacerbate bacterial growth.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a skin condition that causes flaky, oily patches on the scalp, eyebrows, and other areas rich in oil glands. When it affects the eyelids, it can contribute to the development of blepharitis by causing irritation and inflammation of the eyelid margins.
Meibomian Gland Dysfunction
The meibomian glands are located within the eyelids and produce an oily substance that helps prevent tears from evaporating too quickly. When these glands become clogged or dysfunctional, it can result in posterior blepharitis. This dysfunction is often linked to dry eye syndrome, further complicating the condition.
Allergies and Environmental Factors
Allergic reactions to substances such as makeup, contact lens solutions, or airborne allergens can trigger inflammation of the eyelids. Additionally, exposure to environmental irritants like smoke or pollution may worsen symptoms in individuals prone to blepharitis.
Symptoms of Blepharitis
Blepharitis presents a range of symptoms that can vary in severity. Some individuals experience mild discomfort, while others face significant irritation. Common signs include:
- Redness and swelling of the eyelids
- Itching or burning sensations around the eyes
- Crusting or scaling at the base of the eyelashes
- Watery or dry eyes
- A gritty feeling in the eyes
- Sensitivity to light
- Blurred vision
In severe cases, untreated blepharitis can lead to complications such as styes (painful bumps on the eyelid), chalazia (blocked oil glands), or even damage to the cornea.
Diagnosing Blepharitis
Proper diagnosis of blepharitis involves a comprehensive evaluation by an eye care professional. Several steps are typically taken during the diagnostic process:
Medical History Review
The doctor will begin by asking about your medical history, including any existing conditions like seborrheic dermatitis or rosacea. They may also inquire about your lifestyle habits, such as how often you clean your eyelids and whether you wear contact lenses.
Physical Examination
An examination of the eyelids and surrounding areas is crucial for identifying signs of inflammation, crusting, or redness. The doctor may use a magnifying tool called a slit lamp to get a closer look at the eyelid margins and assess the health of the meibomian glands.
Testing for Underlying Conditions
In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to rule out other conditions that mimic blepharitis. For example, a tear film analysis might be conducted to check for dry eye syndrome, which often coexists with posterior blepharitis.
Treatment Options for Blepharitis
While there is no definitive cure for blepharitis, various treatments can effectively manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups. Treatment plans are tailored to the specific type and severity of the condition.
Eyelid Hygiene Practices
One of the most important aspects of managing blepharitis is maintaining good eyelid hygiene. This includes:
- Washing the eyelids with warm water and a gentle cleanser twice daily
- Using a warm compress to loosen crusts and debris along the eyelid margins
- Gently scrubbing the eyelids with a cotton swab or specialized eyelid wipes
Consistent eyelid hygiene helps remove bacteria, oils, and dead skin cells that contribute to inflammation.
Medicated Eye Drops and Ointments
For more severe cases, doctors may prescribe medicated eye drops or ointments to alleviate symptoms. Antibiotic drops or ointments are commonly used to treat bacterial infections, while steroid-based medications may be recommended to reduce inflammation. Artificial tears can also provide relief for dry eyes associated with blepharitis.
Oral Medications
In certain situations, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to address widespread bacterial infections or meibomian gland dysfunction. These medications work systemically to target the root cause of the inflammation.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making simple changes to your daily routine can help minimize the risk of blepharitis flare-ups:
- Avoid using heavy makeup or skincare products near the eyes
- Replace eye makeup regularly to prevent bacterial buildup
- Stay hydrated to support overall eye health
- Protect your eyes from environmental irritants by wearing sunglasses outdoors
Advanced Treatments
For individuals who do not respond well to conventional treatments, advanced therapies may be considered. Examples include:
- LipiFlow: A device designed to unclog meibomian glands and improve tear quality
- Intense Pulsed Light Therapy: A non-invasive procedure that reduces inflammation and stimulates gland function
These treatments are typically reserved for chronic or refractory cases of blepharitis.
Preventing Blepharitis Flare-Ups
While it may not always be possible to prevent blepharitis entirely, adopting preventive measures can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Key strategies include:
- Practicing regular eyelid hygiene
- Avoiding known allergens and irritants
- Managing underlying conditions like seborrheic dermatitis or rosacea
- Scheduling routine eye exams to monitor eye health
By staying proactive and working closely with an eye care professional, individuals with blepharitis can achieve better control over their symptoms and enjoy improved quality of life.