Tinnitus, often abbreviated as “TI,” is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the perception of sound in the ears or head without any external source. This phantom noise can manifest as ringing, buzzing, hissing, or even roaring sounds, and it can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. While tinnitus is not a disease itself, it is often a symptom of an underlying issue, such as hearing loss, ear injury, or a circulatory system disorder. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and various management options available for those living with tinnitus.
Understanding Tinnitus
Tinnitus is a complex condition that affects individuals differently. For some, it may be a mild annoyance that comes and goes, while for others, it can be a constant and debilitating presence. Understanding what tinnitus is and how it affects people is the first step toward finding effective ways to manage it.
What Happens in the Ear and Brain?
Tinnitus occurs when there is a disruption in the auditory system, which includes the ear, the auditory nerve, and the parts of the brain that process sound. Normally, sound waves travel through the ear and are converted into electrical signals that the brain interprets as sound. However, when something interferes with this process, the brain may misinterpret signals or amplify certain sounds, leading to the perception of noise that does not exist externally.
Causes of Tinnitus
The exact cause of tinnitus can vary from person to person, and in many cases, it may result from a combination of factors. Below are some of the most common causes of tinnitus:
Hearing Loss
One of the most prevalent causes of tinnitus is hearing loss, particularly age-related hearing loss. As people grow older, the delicate hair cells in the inner ear that help transmit sound signals to the brain can become damaged or die off. This damage can lead to hearing loss and, in many cases, tinnitus. Noise-induced hearing loss, caused by prolonged exposure to loud sounds, is another common contributor to tinnitus.
Ear Infections and Blockages
- Ear Infections: Infections in the ear, whether in the outer, middle, or inner ear, can cause inflammation and fluid buildup, leading to tinnitus.
- Earwax Buildup: Excessive earwax can block the ear canal and cause pressure on the eardrum, resulting in tinnitus symptoms.
Medications
Certain medications can have side effects that include tinnitus. These medications are often referred to as ototoxic drugs because they can damage the ear or auditory nerve. Common examples include high doses of aspirin, certain antibiotics, diuretics, and chemotherapy drugs. If you suspect that your medication is causing tinnitus, consult your healthcare provider before making any changes.
Underlying Health Conditions
Tinnitus can also be a symptom of various health conditions, including:
- Meniere’s Disease: A disorder of the inner ear that affects balance and hearing.
- Temporomandibular Joint Disorders: Problems with the jaw joint can sometimes lead to tinnitus.
- Blood Vessel Disorders: Conditions such as high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, or turbulent blood flow near the ear can cause pulsatile tinnitus, where the sound is rhythmic and matches the heartbeat.
Symptoms of Tinnitus
Tinnitus symptoms can vary widely in terms of intensity, frequency, and type of sound perceived. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms that do not interfere with daily life, while others may find their symptoms overwhelming. Below are some common symptoms associated with tinnitus:
Types of Sounds
- Ringing
- Buzzing
- Hissing
- Roaring
- Clicking
Impact on Daily Life
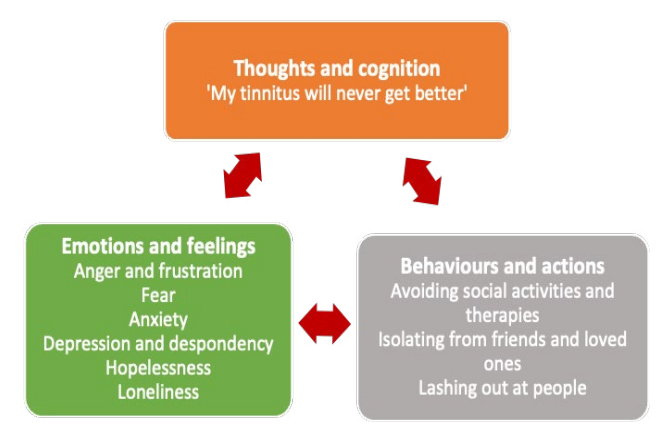
Tinnitus can have a profound impact on mental and emotional well-being. Many individuals report difficulty concentrating, sleeping, or relaxing due to the constant presence of noise. Over time, this can lead to anxiety, depression, irritability, and fatigue. The severity of these effects often depends on the individual’s ability to cope with the condition.
Management Options for Tinnitus
While there is currently no cure for tinnitus, there are several management strategies that can help reduce its impact and improve quality of life. These options range from lifestyle changes to medical interventions, and they are often tailored to the individual’s specific needs and symptoms.
Hearing Aids
For individuals with hearing loss, hearing aids can be an effective way to manage tinnitus. By amplifying external sounds, hearing aids can help mask the internal noise caused by tinnitus. Additionally, some modern hearing aids come equipped with built-in tinnitus masking features that produce soothing sounds to distract from the tinnitus.
Sound Therapy
Sound therapy involves using external sounds to help distract from or mask the perception of tinnitus. This can include:
- White Noise Machines: Devices that produce calming background noise, such as rain or ocean waves.
- Fans or Humidifiers: Household items that create consistent ambient noise.
- Tinnitus Maskers: Small devices worn in or around the ear that emit low-level sounds to counteract tinnitus.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy is a form of counseling that helps individuals change their negative thought patterns and behaviors related to tinnitus. By learning coping strategies and relaxation techniques, patients can reduce the emotional distress caused by tinnitus and improve their overall quality of life.
Tinnitus Retraining Therapy
Tinnitus retraining therapy combines sound therapy with counseling to help individuals habituate to the presence of tinnitus. Over time, this approach aims to make the noise less noticeable and less bothersome. It typically involves wearing a device that emits low-level sounds and attending regular counseling sessions.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can also help manage tinnitus symptoms. Consider the following tips:
- Avoid Loud Noises: Protect your ears from loud sounds by using earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments.
- Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate tinnitus symptoms, so practicing relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga may be beneficial.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Both substances can worsen tinnitus in some individuals, so reducing intake may help.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Poor sleep can increase the perception of tinnitus, so establishing a healthy sleep routine is important.
Medical Treatments
In some cases, addressing the underlying cause of tinnitus can alleviate symptoms. For example:
- If tinnitus is caused by an ear infection, treating the infection with antibiotics may resolve the issue.
- If earwax buildup is the culprit, having the wax professionally removed can provide relief.
- For individuals with blood vessel disorders, medications or surgical procedures may be necessary to address the root cause.
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals explore alternative therapies to manage their tinnitus symptoms. While scientific evidence supporting these methods is limited, they may offer relief for certain people. Examples include:
- Acupuncture: A traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body.
- Herbal Supplements: Some people use supplements like ginkgo biloba, though their effectiveness is not well-established.
- Mindfulness Meditation: Practicing mindfulness can help individuals focus less on their tinnitus and more on the present moment.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you are experiencing tinnitus, it is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and discuss appropriate treatment options. You should seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Sudden onset of tinnitus, especially in one ear only
- Hearing loss or dizziness accompanying tinnitus
- Tinnitus after a head or neck injury
Audiologists, ENT specialists, and other healthcare providers can conduct tests to evaluate your hearing and identify potential causes of tinnitus. Based on their findings, they can recommend personalized management strategies to help you cope with the condition.





