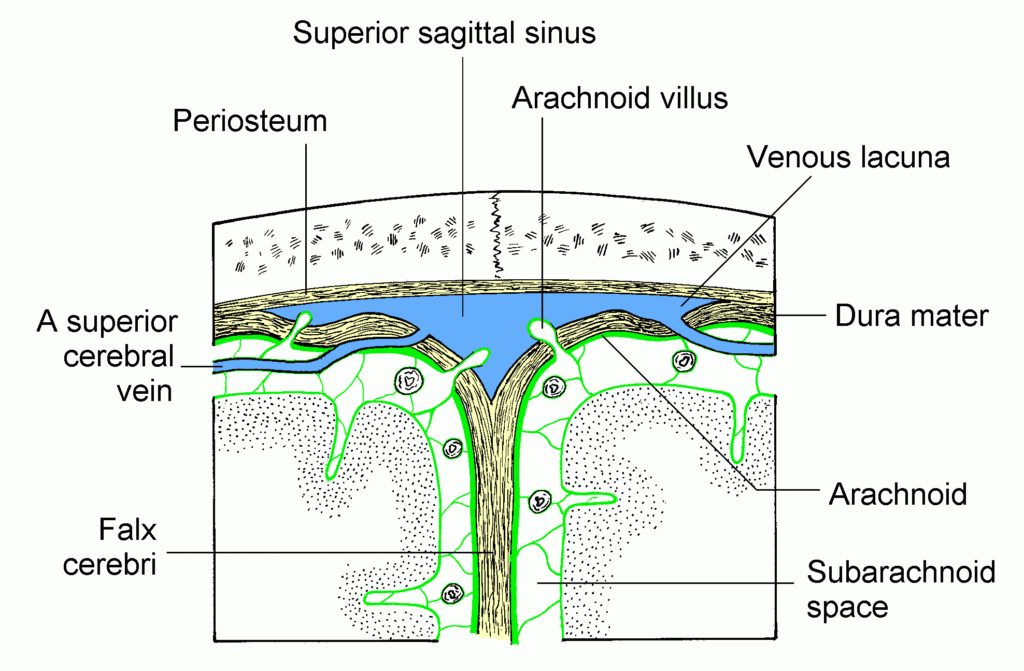
A subarachnoid hemorrhage, often abbreviated as SAH, is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when bleeding happens in the space between the brain and the tissues surrounding it. This type of bleeding can lead to severe complications and requires immediate medical attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for this condition is essential for both patients and healthcare providers.
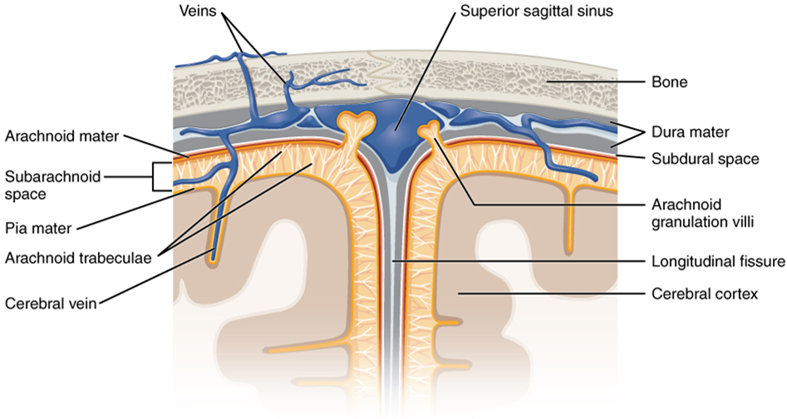
What Happens During a Subarachnoid Hemorrhage?
The brain is protected by several layers of tissue, one of which is called the arachnoid membrane. The space beneath this membrane is filled with cerebrospinal fluid, which cushions the brain and helps maintain its stability. When blood leaks into this area, it disrupts the normal functioning of the brain and can cause significant damage.
The most common cause of bleeding in this space is the rupture of an abnormal bulge in a blood vessel, known as an aneurysm. However, other factors such as trauma, certain medical conditions, or even unknown causes can also lead to this type of hemorrhage.
Causes of Bleeding in the Space Around the Brain
- Ruptured Aneurysm: A weak spot in a blood vessel wall can balloon out and eventually burst, leading to bleeding. This is the most frequent cause of subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Trauma: Head injuries from accidents, falls, or violent impacts can cause blood vessels to tear, resulting in bleeding.
- Blood Vessel Disorders: Conditions like arteriovenous malformations, where blood vessels are abnormally formed, can increase the risk of bleeding.
- Bleeding Disorders: Certain diseases or medications that affect blood clotting can make individuals more prone to hemorrhages.
- Unknown Causes: In some cases, despite thorough investigation, the exact reason for the bleeding remains unclear.
Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the symptoms of bleeding in the space around the brain is critical, as early intervention can save lives. Some of the most common signs include:
- Sudden and Severe Headache: Often described as the “worst headache of one’s life,” this pain typically comes on abruptly and is unlike any other headache experienced before.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms often accompany the headache and may indicate increased pressure within the skull.
- Stiff Neck: Difficulty moving the neck or stiffness can occur due to irritation of the meninges, the protective layers around the brain.
- Loss of Consciousness: In severe cases, individuals may faint or become unresponsive.
- Seizures: Uncontrolled electrical activity in the brain can lead to seizures, which are a sign of significant neurological distress.
- Vision Changes: Blurred or double vision, sensitivity to light, or other visual disturbances may occur.
- Confusion or Altered Mental State: Difficulty thinking clearly, memory problems, or unusual behavior can signal brain dysfunction.
Diagnosing the Condition
When a patient presents with symptoms suggestive of bleeding in the space around the brain, healthcare providers will conduct a series of tests to confirm the diagnosis and determine the underlying cause. These diagnostic tools include:
- Computed Tomography Scan: Also known as a CT scan, this imaging test is often the first step in diagnosing a subarachnoid hemorrhage. It can quickly identify the presence of blood in the brain.
- Lumbar Puncture: If the CT scan does not show clear evidence of bleeding but suspicion remains high, a lumbar puncture may be performed. This involves collecting a sample of cerebrospinal fluid to check for traces of blood.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An MRI provides detailed images of the brain and can help identify abnormalities such as aneurysms or arteriovenous malformations.
- Cerebral Angiography: This specialized imaging technique allows doctors to visualize the blood vessels in the brain and locate the source of the bleeding.
Treatment Options
The treatment for bleeding in the space around the brain depends on the severity of the condition, the underlying cause, and the overall health of the patient. Immediate medical care is crucial to prevent further complications and improve outcomes. Common treatment approaches include:
- Surgical Intervention: In cases where an aneurysm has ruptured, surgery may be necessary to repair the damaged blood vessel. Two common procedures are clipping, where a metal clip is placed at the base of the aneurysm to stop the bleeding, and coiling, where tiny platinum coils are inserted into the aneurysm to block blood flow.
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-seizure drugs, and medications to manage blood pressure are often prescribed to stabilize the patient and reduce the risk of additional complications.
- Monitoring and Supportive Care: Patients may require close monitoring in an intensive care unit to manage symptoms such as increased intracranial pressure or complications like hydrocephalus, a buildup of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain.
- Rehabilitation: After the acute phase of treatment, many individuals will need physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech therapy to regain lost abilities and improve their quality of life.
Potential Complications
Bleeding in the space around the brain can lead to several serious complications, including:
- Rebleeding: If the source of the bleeding is not addressed promptly, there is a risk of the blood vessel rupturing again, which can be fatal.
- Vasospasm: Narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain can occur days after the initial hemorrhage, reducing blood flow and causing further damage.
- Hydrocephalus: Excess cerebrospinal fluid can accumulate in the brain, increasing pressure and leading to additional neurological issues.
- Permanent Brain Damage: Depending on the extent of the bleeding and the timeliness of treatment, some individuals may experience long-term cognitive or physical impairments.
Understanding these potential complications underscores the importance of seeking immediate medical attention if symptoms arise and adhering closely to the recommended treatment plan.
Preventive Measures
While not all cases of bleeding in the space around the brain can be prevented, certain steps can reduce the risk of developing this condition:
- Managing High Blood Pressure: Keeping blood pressure under control through lifestyle changes and medication can lower the likelihood of aneurysm formation or rupture.
- Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Both habits have been linked to an increased risk of aneurysms and should be avoided.
- Regular Medical Checkups: Routine screenings can help detect underlying conditions that might predispose someone to this type of hemorrhage.
- Wearing Protective Gear: Using helmets during sports or activities that pose a risk of head injury can prevent trauma-related bleeding.
By taking proactive measures and staying informed about the risks and warning signs, individuals can better protect themselves and their loved ones from this devastating condition.