Somatic Symptom Disorder, often abbreviated as SSD, is a complex mental health condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It is characterized by an intense focus on physical symptoms, such as pain or fatigue, which causes significant emotional distress and disrupts daily life. While the exact cause of this disorder remains unclear, it is believed to stem from a combination of biological, psychological, and social factors. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of Somatic Symptom Disorder, its symptoms, how it is diagnosed, and the available treatment options.
What Is Somatic Symptom Disorder?
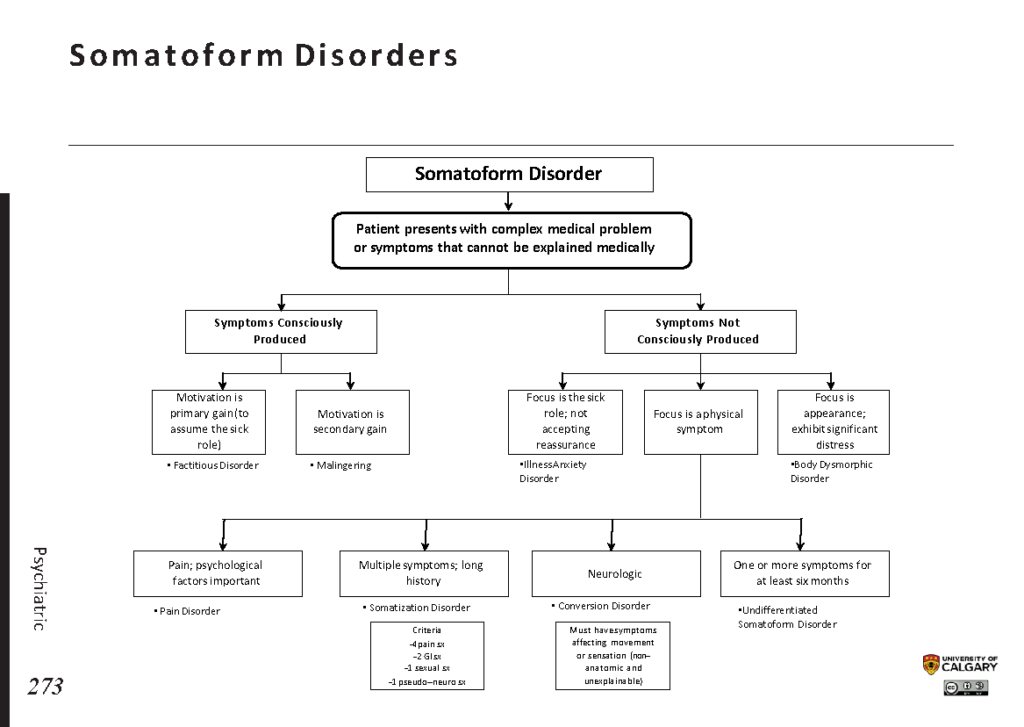
Somatic Symptom Disorder is a condition where individuals experience one or more physical symptoms that are distressing and lead to excessive thoughts, feelings, or behaviors related to those symptoms. Unlike other medical conditions, the severity of the symptoms often does not match the underlying medical findings. This discrepancy can make it challenging for healthcare providers to diagnose and treat the condition effectively.
It is important to note that people with this disorder are not “faking” their symptoms. The physical sensations they experience are very real and can be debilitating. However, the way they perceive and respond to these symptoms tends to amplify their distress, leading to a cycle of anxiety and worsening symptoms.
Key Features of the Disorder
- Persistent Physical Symptoms: These can include pain, gastrointestinal issues, fatigue, or neurological complaints.
- Excessive Thoughts: Individuals may spend a significant amount of time worrying about the seriousness of their symptoms.
- Emotional Distress: The symptoms often lead to feelings of anxiety, sadness, or frustration.
- Behavioral Changes: People may frequently visit doctors, undergo multiple tests, or avoid certain activities due to fear of worsening their symptoms.
Common Symptoms of Somatic Symptom Disorder
The symptoms of this condition can vary widely from person to person. Some individuals may experience only one persistent symptom, while others may have multiple symptoms that fluctuate over time. Below are some of the most common symptoms associated with the disorder:
Physical Symptoms
- Pain: Chronic pain in various parts of the body, such as headaches, back pain, or joint pain, is one of the most frequently reported symptoms.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Symptoms like nausea, bloating, diarrhea, or constipation are common.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness that does not improve with rest is another hallmark of the condition.
- Neurological Complaints: These may include dizziness, weakness, or difficulty concentrating.
Psychological Symptoms
- Anxiety: Excessive worry about the meaning or cause of physical symptoms.
- Depression: Feelings of hopelessness or sadness due to the impact of symptoms on daily life.
- Hypervigilance: Constant monitoring of bodily sensations for signs of illness.
Behavioral Symptoms
- Frequent Doctor Visits: Seeking reassurance from healthcare providers or undergoing unnecessary tests.
- Avoidance: Steering clear of activities or situations that might trigger symptoms.
- Dependency: Relying heavily on family members or friends for support due to perceived limitations caused by symptoms.
How Is Somatic Symptom Disorder Diagnosed?
Diagnosing this condition can be challenging because the symptoms often overlap with those of other medical or mental health disorders. Healthcare providers typically follow a systematic approach to rule out other potential causes before making a diagnosis.
Medical Evaluation
The first step in diagnosing the condition involves a thorough medical evaluation. This includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests to identify any underlying medical conditions that could explain the symptoms. Blood tests, imaging studies, and other investigations may be conducted to rule out diseases such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, or autoimmune conditions.
Psychological Assessment
If no clear medical explanation is found, a psychological assessment may be recommended. Mental health professionals use interviews and standardized questionnaires to evaluate the individual’s thoughts, emotions, and behaviors related to their symptoms. Key factors considered during the assessment include:
- The duration and intensity of the symptoms.
- The level of distress caused by the symptoms.
- The impact of the symptoms on daily functioning.
Differential Diagnosis
It is crucial to differentiate Somatic Symptom Disorder from other conditions that share similar features. These may include:
- Conversion Disorder: A condition where psychological stress manifests as neurological symptoms, such as paralysis or blindness.
- Illness Anxiety Disorder: Previously known as hypochondriasis, this involves excessive worry about having a serious illness despite minimal or no symptoms.
- Chronic Pain Syndrome: Persistent pain that continues beyond the usual recovery period.
Treatment Options for Somatic Symptom Disorder
Treating this condition requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of the disorder. The goal of treatment is not necessarily to eliminate the symptoms but to help individuals manage them more effectively and improve their quality of life.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy, is one of the most effective treatments for this condition. It helps individuals:
- Identify and challenge negative thought patterns related to their symptoms.
- Develop healthier coping strategies to manage stress and anxiety.
- Gradually reduce avoidance behaviors and regain confidence in their abilities.
Medication
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to alleviate specific symptoms or co-occurring conditions such as depression or anxiety. Commonly used medications include:
- Antidepressants: These can help regulate mood and reduce the perception of pain.
- Anxiolytics: Medications that reduce anxiety may be used on a short-term basis.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in managing the condition. These include:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can improve mood, reduce stress, and enhance overall well-being.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet can support physical health and energy levels.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga can help individuals cope with stress more effectively.
Support Systems
Building a strong support system is essential for individuals with this condition. Family, friends, and support groups can provide encouragement, understanding, and practical assistance. Additionally, involving loved ones in the treatment process can foster better communication and reduce feelings of isolation.
Living with Somatic Symptom Disorder
While living with this condition can be challenging, many individuals find ways to manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. Education about the disorder is a critical first step, as it helps individuals understand that their symptoms are real and valid, even if they do not have a clear medical explanation.
Open communication with healthcare providers is also vital. Establishing a trusting relationship with a primary care physician or mental health professional can ensure that individuals receive consistent and compassionate care. Regular check-ins can help monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Tips for Coping
- Keep a symptom diary to track triggers and patterns.
- Set realistic goals for daily activities and celebrate small achievements.
- Practice self-compassion and avoid self-criticism.
- Seek professional help if symptoms worsen or interfere significantly with daily life.
Raising Awareness and Reducing Stigma
Despite its prevalence, Somatic Symptom Disorder is often misunderstood and stigmatized. Many people mistakenly believe that individuals with this condition are exaggerating their symptoms or seeking attention. Such misconceptions can prevent those affected from seeking help and receiving proper care.
Efforts to raise awareness about the disorder are essential to combat stigma and promote understanding. Educational campaigns, community outreach programs, and advocacy initiatives can play a significant role in dispelling myths and encouraging open conversations about mental health.
How You Can Help
- Educate yourself and others about the condition.
- Listen without judgment when someone shares their experiences.
- Encourage individuals to seek professional help if needed.
- Advocate for improved access to mental health services in your community.