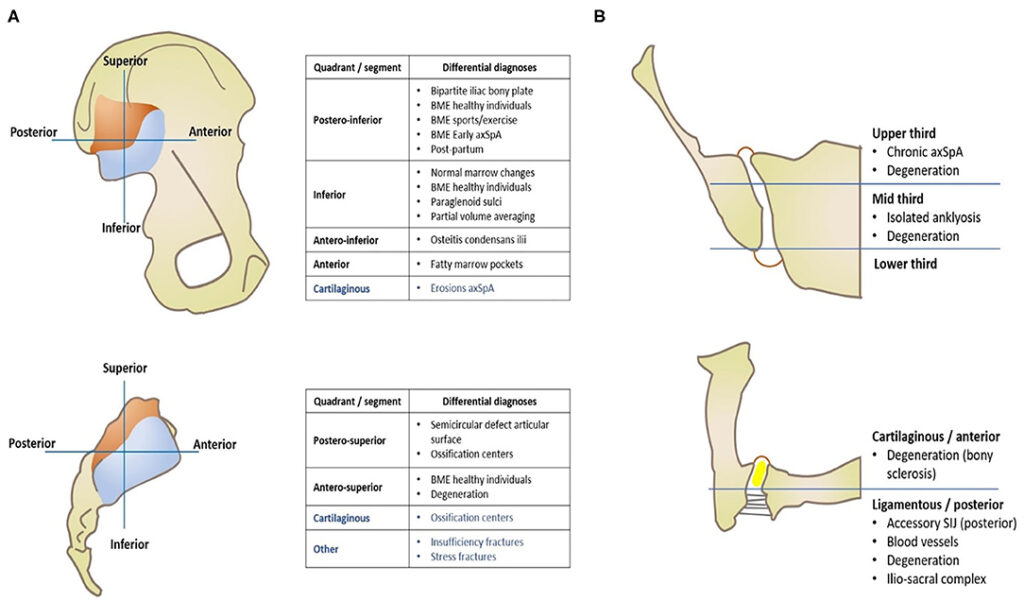
Sacroiliitis, often abbreviated as SI, refers to the inflammation of the sacroiliac joint. This condition can cause significant discomfort and may interfere with daily activities. The sacroiliac joint connects the lower part of the spine to the pelvis, playing a crucial role in weight distribution and movement. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments for this condition is essential for effective management and relief.
Understanding the Sacroiliac Joint
The sacroiliac joint is located where the spine meets the pelvis. It consists of two joints that connect the triangular bone at the base of the spine, known as the sacrum, to the iliac bones on either side of the pelvis. These joints are supported by strong ligaments and muscles, making them relatively stable. However, they are still susceptible to inflammation and injury, which can lead to sacroiliitis.
Function of the Sacroiliac Joint
- Weight Distribution: The sacroiliac joint helps transfer weight from the upper body to the lower limbs during activities such as walking or standing.
- Mobility: While the joint has limited mobility, it allows for slight movements that contribute to flexibility and shock absorption.
Causes of Inflammation in the Sacroiliac Joint
There are several factors that can lead to inflammation in the sacroiliac joint. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan.
Inflammatory Conditions
One of the most common causes of sacroiliitis is inflammatory conditions. These include:
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: A type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine and can lead to severe stiffness and pain.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: A form of arthritis associated with the skin condition psoriasis, causing joint pain and swelling.
- Reactive Arthritis: A condition that occurs in response to an infection elsewhere in the body, leading to joint inflammation.
Injury or Trauma
Physical trauma to the sacroiliac joint can result in inflammation. Common causes include:
- Falls: A fall directly onto the buttocks can injure the joint.
- Car Accidents: Whiplash or impact injuries can affect the sacroiliac joint.
- Pregnancy: The added weight and changes in posture during pregnancy can strain the joint, leading to inflammation.
Infection
In rare cases, an infection in the sacroiliac joint can cause inflammation. Bacterial infections may spread to the joint from other parts of the body, leading to pain and swelling.
Other Contributing Factors
Additional factors that may contribute to sacroiliitis include:
- Osteoarthritis: Wear and tear of the joint over time can lead to inflammation.
- Gout: A buildup of uric acid crystals in the joint can cause sudden and severe pain.
- Obesity: Excess weight places additional stress on the joint, increasing the risk of inflammation.
Symptoms of Sacroiliitis
The symptoms of sacroiliitis can vary depending on the severity and underlying cause of the inflammation. Recognizing these symptoms early can help in seeking timely medical attention.
Pain in the Lower Back and Buttocks
One of the hallmark symptoms of sacroiliitis is pain in the lower back and buttocks. This pain may be localized to one side or affect both sides of the body. It is often described as dull and achy but can become sharp and intense with certain movements.
Radiating Pain
In some cases, the pain may radiate to other areas of the body, including:
- Hip Area: Pain may extend to the hips, making it difficult to walk or stand for long periods.
- Thighs: Discomfort may travel down the back of the thighs, mimicking sciatica.
- Groin: Some individuals may experience pain in the groin area.
Stiffness and Reduced Mobility
Inflammation in the sacroiliac joint can lead to stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity such as sleeping or sitting for extended periods. This stiffness can limit mobility and make everyday tasks challenging.
Pain Aggravated by Movement
Certain activities can worsen the pain associated with sacroiliitis. These include:
- Climbing Stairs: The repetitive motion of climbing stairs can strain the joint.
- Standing for Long Periods: Prolonged standing can exacerbate discomfort.
- Twisting or Bending: Movements that involve twisting or bending the spine can aggravate the joint.
Diagnosis of Sacroiliitis
Diagnosing sacroiliitis involves a combination of physical examinations, imaging tests, and sometimes laboratory tests to rule out other conditions.
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will perform a physical examination to assess pain levels, range of motion, and areas of tenderness. They may apply pressure to specific points on the pelvis to identify the source of discomfort.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are often used to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the extent of inflammation. These may include:
- X-rays: To check for signs of joint damage or abnormalities.
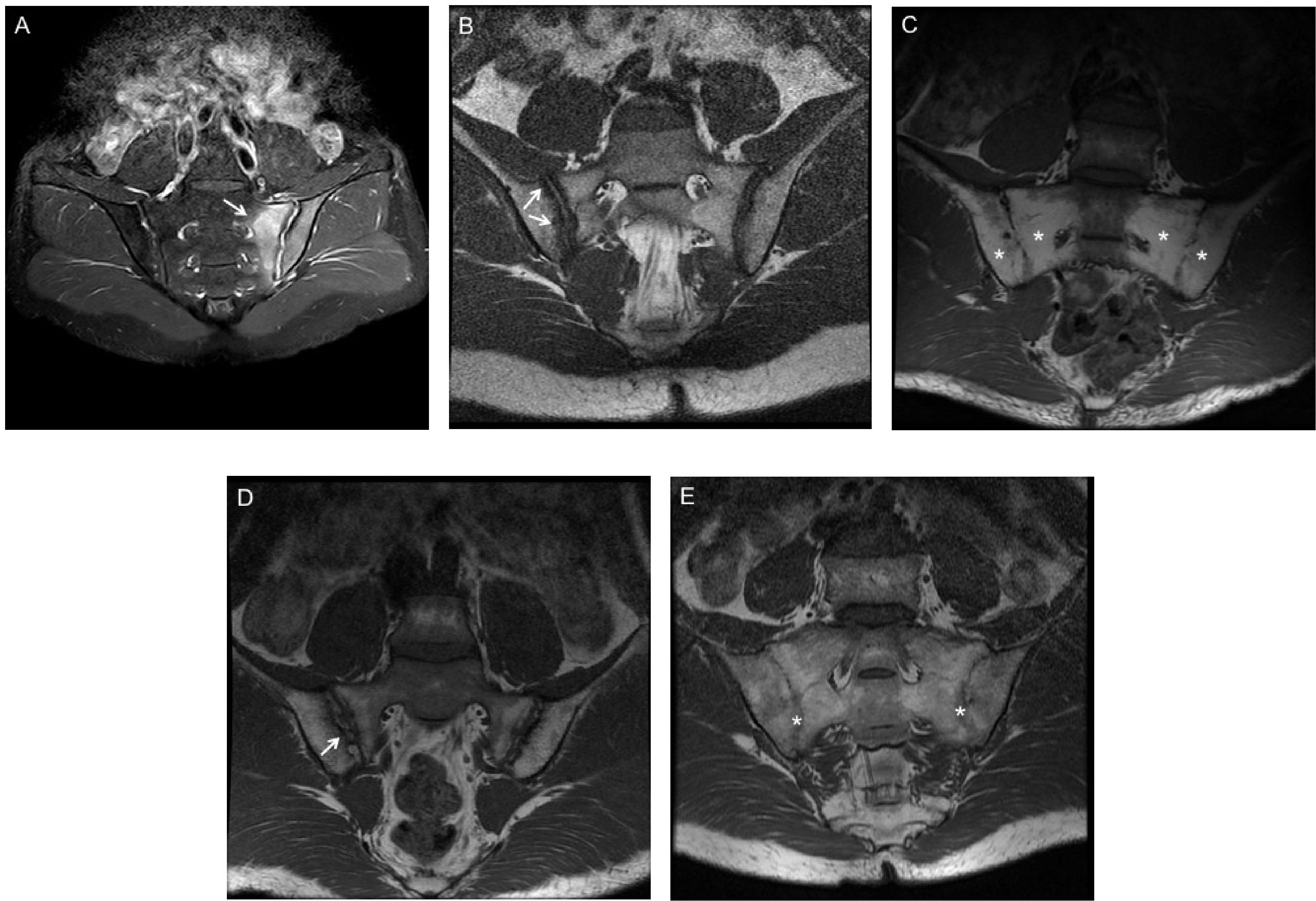
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of soft tissues and can detect early signs of inflammation.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Offers a more detailed view of the bones and joints.
Laboratory Tests
In cases where an underlying inflammatory condition is suspected, blood tests may be ordered to check for markers of inflammation or autoimmune disorders.
Treatment Options for Sacroiliitis
Treatment for sacroiliitis aims to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and improve mobility. The approach may vary depending on the severity of the condition and its underlying cause.
Medications
Several medications can help manage the symptoms of sacroiliitis:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter options like ibuprofen or naproxen can reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Administered directly into the joint, these injections provide targeted relief for severe pain.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Used for inflammatory conditions like ankylosing spondylitis to slow disease progression.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in managing sacroiliitis. A therapist can design a personalized exercise program to:
- Strengthen Supporting Muscles: Exercises targeting the core, back, and pelvic muscles can stabilize the joint.
- Improve Flexibility: Stretching routines can enhance mobility and reduce stiffness.
- Correct Posture: Proper alignment can alleviate stress on the sacroiliac joint.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold to the affected area can provide temporary relief:
- Heat Therapy: Helps relax muscles and improve blood flow to the joint.
- Cold Therapy: Reduces inflammation and numbs sharp pain.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can also aid in managing sacroiliitis:
- Weight Management: Losing excess weight can reduce pressure on the joint.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Using supportive chairs or cushions can minimize strain during daily activities.
- Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate the joint can prevent further irritation.
Surgical Interventions
In rare cases where conservative treatments fail, surgery may be considered. Procedures such as joint fusion can stabilize the sacroiliac joint and relieve chronic pain.
Living with Sacroiliitis
While sacroiliitis can be challenging to manage, understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options empowers individuals to take control of their health. By working closely with healthcare providers and adopting a proactive approach, it is possible to minimize the impact of this condition on daily life.