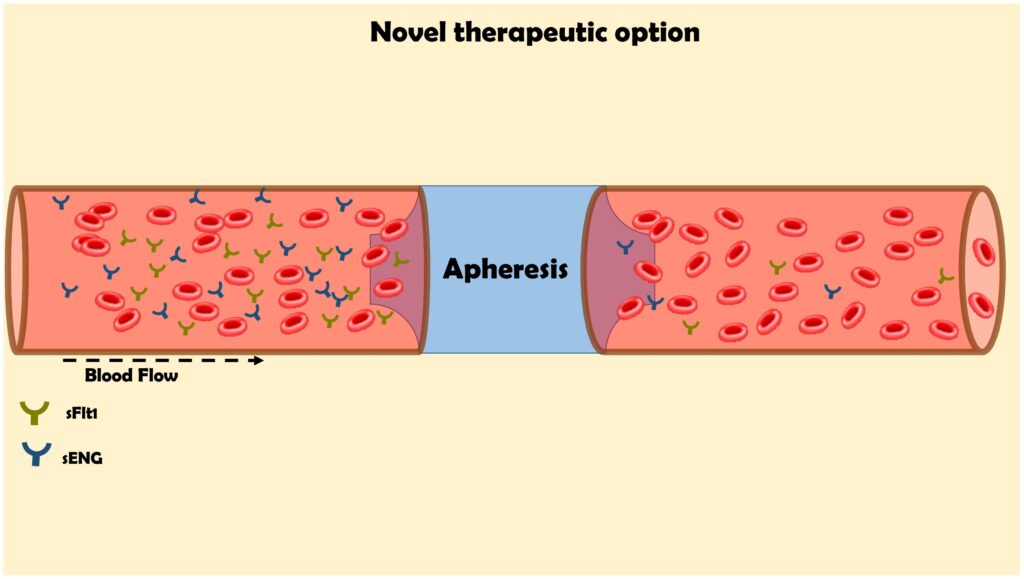
Pregnancy is a time of joy and anticipation, but it can also bring challenges that require careful attention. One such challenge is preeclampsia, often abbreviated as PE. This condition, characterized by high blood pressure and potential damage to other organs, affects pregnant women and can pose risks to both the mother and the baby. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and management strategies is crucial for ensuring a healthy pregnancy. In this guide, we will explore everything you need to know about this serious condition.
What Is Preeclampsia?
Preeclampsia is a medical condition that typically occurs after the twentieth week of pregnancy. It is marked by elevated blood pressure levels and signs of damage to organs, most commonly the liver and kidneys. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications for both the mother and the unborn child.
Key Characteristics of Preeclampsia
- Sudden increase in blood pressure
- Presence of protein in the urine, indicating kidney problems
- Swelling in the hands, feet, and face
- Headaches and visual disturbances
- Upper abdominal pain, often under the ribs on the right side
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of preeclampsia remains unclear, but researchers believe it may stem from issues related to the placenta. The placenta is the organ that nourishes the baby during pregnancy. In women with preeclampsia, the blood vessels that supply the placenta may not develop or function properly, leading to restricted blood flow.
Potential Causes
- Abnormal development of placental blood vessels
- Immune system issues affecting the mother’s response to pregnancy
- Genetic factors passed down through family history
- Insufficient blood flow to the uterus
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing preeclampsia. These include:
- First-time pregnancy
- History of preeclampsia in previous pregnancies
- Chronic high blood pressure before pregnancy
- Obesity or being significantly overweight
- Carrying multiple babies, such as twins or triplets
- Diabetes or kidney disease prior to pregnancy
- Age younger than twenty or older than forty
Signs and Symptoms of Preeclampsia
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of preeclampsia early can help prevent complications. While some symptoms are mild, others may indicate a more severe form of the condition.
Common Symptoms
- High blood pressure readings consistently above normal levels
- Excessive swelling, particularly in the hands and face
- Sudden weight gain over a short period
- Severe headaches that do not improve with medication
- Changes in vision, such as blurred vision, light sensitivity, or temporary loss of sight
- Pain in the upper abdomen, often described as feeling like heartburn
- Nausea or vomiting in the second half of pregnancy
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the following symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately:
- Severe headache that does not go away
- Difficulty breathing or chest pain
- Decreased urination
- Unusual changes in vision
- Persistent pain in the upper abdomen
Complications Associated with Preeclampsia
If preeclampsia is not managed effectively, it can lead to serious complications for both the mother and the baby. Understanding these risks underscores the importance of regular prenatal care.
Complications for the Mother
- Eclampsia, a condition where seizures occur due to extremely high blood pressure
- Hellp syndrome, a life-threatening liver and blood-clotting disorder
- Stroke caused by uncontrolled hypertension
- Kidney failure or permanent damage to the kidneys
- Placental abruption, where the placenta separates from the uterine wall prematurely
Complications for the Baby
- Growth restriction due to reduced blood flow to the placenta
- Preterm birth, which can result in respiratory and developmental issues
- Low birth weight
- Stillbirth in severe cases
Diagnosis of Preeclampsia
Regular prenatal visits are essential for monitoring the health of both the mother and the baby. During these appointments, healthcare providers check for signs of preeclampsia through various tests and examinations.
Diagnostic Tests
- Blood pressure measurements at every visit
- Urine tests to detect the presence of protein
- Blood tests to assess liver and kidney function
- Ultrasound scans to evaluate fetal growth and amniotic fluid levels
- Non-stress tests or biophysical profiles to monitor the baby’s well-being
Treatment Options for Preeclampsia
The only definitive cure for preeclampsia is the delivery of the baby. However, if the condition develops early in pregnancy, doctors may recommend managing symptoms until the baby is mature enough for delivery.
Management Strategies
- Frequent monitoring of blood pressure and urine protein levels
- Medications to lower blood pressure and prevent seizures
- Bed rest to reduce stress on the body
- Close observation of fetal development through ultrasounds
- Early delivery if the condition worsens or poses significant risks
Delivery as a Treatment
In cases where preeclampsia becomes severe, delivering the baby may be necessary, even if it means an early birth. The timing of delivery depends on the severity of the condition and the baby’s gestational age. Doctors weigh the risks of continuing the pregnancy against the risks of preterm birth when making this decision.
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
While preeclampsia cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle modifications and preventive measures may reduce the risk or severity of the condition.
Lifestyle Tips
- Maintain a healthy weight before and during pregnancy
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Avoid excessive salt intake to help manage blood pressure
- Exercise regularly, as recommended by your healthcare provider
- Attend all prenatal appointments for timely detection of potential issues
Medical Interventions
In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend low-dose aspirin for women at high risk of developing preeclampsia. This medication has been shown to reduce the likelihood of the condition in certain individuals. Always consult your doctor before starting any new treatment during pregnancy.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Dealing with preeclampsia can be emotionally challenging for expectant mothers. The uncertainty and potential risks associated with the condition may lead to anxiety and stress. It is important to address these feelings and seek support when needed.
Coping Strategies
- Communicate openly with your healthcare provider about your concerns
- Join support groups for women experiencing similar challenges
- Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation
- Lean on family and friends for emotional support
- Educate yourself about the condition to feel more in control
Final Thoughts
Preeclampsia is a complex and potentially serious condition that requires vigilance and proactive management. By understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and working closely with healthcare providers, women can navigate this challenge and protect the health of themselves and their babies.