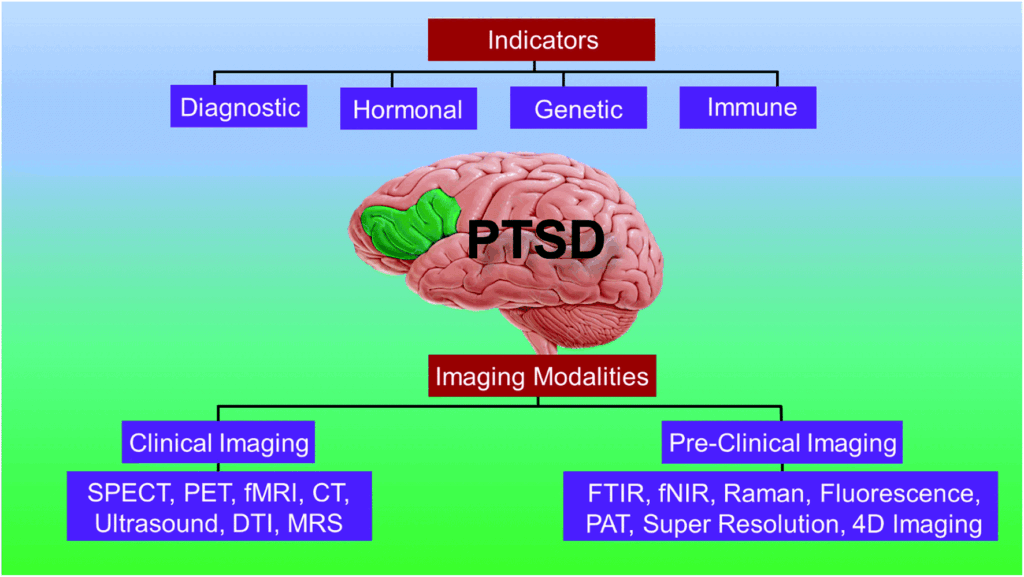
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder, commonly known as PTSD, is a mental health condition that affects individuals who have experienced or witnessed traumatic events. It can disrupt daily life, relationships, and emotional well-being, making it crucial to understand its causes, recognize its symptoms, and explore effective treatments. This article delves into the complexities of this condition, offering insights into how it develops, how it manifests, and how it can be managed.
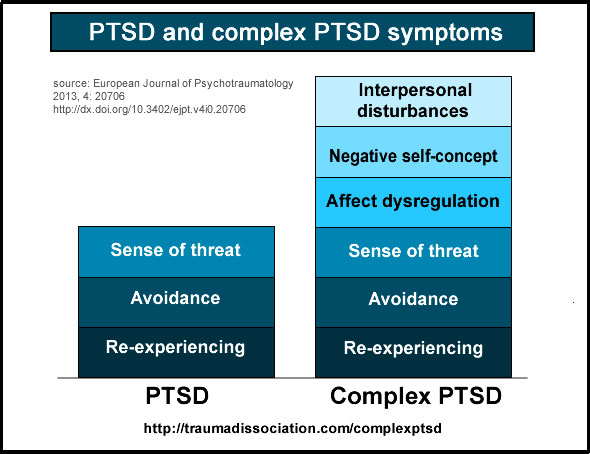
Understanding Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder is a psychological response to trauma. Unlike normal stress or anxiety, this condition persists long after the traumatic event has ended. The impact of such experiences can linger, causing significant distress and impairing an individual’s ability to function normally. While it is often associated with military veterans, anyone who has faced a life-threatening or deeply disturbing situation can develop this disorder.
What Happens During a Traumatic Event?
A traumatic event is any situation that causes intense fear, helplessness, or horror. Examples include natural disasters, serious accidents, violent assaults, or the sudden loss of a loved one. During such events, the body’s “fight or flight” response is activated, releasing stress hormones like adrenaline to prepare for immediate action. While this response is essential for survival, in some cases, the mind and body struggle to return to a state of normalcy afterward, leading to the development of this condition.
Causes of Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
The causes of this condition are complex and multifaceted. They involve a combination of environmental, psychological, and biological factors. Below are some of the primary contributors:
Exposure to Trauma
The most direct cause of this condition is exposure to a traumatic event. These events can vary widely in nature but often involve situations where an individual feels their life or safety is threatened. Common examples include:
- Combat exposure during military service
- Physical or sexual assault
- Natural disasters like earthquakes or hurricanes
- Serious accidents such as car crashes or fires
- Witnessing violence or death
It is important to note that not everyone who experiences trauma will develop this condition. Factors such as personal resilience, support systems, and prior mental health history play a role in determining vulnerability.
Genetic and Biological Factors
Research suggests that genetics may influence an individual’s susceptibility to developing this condition. Some people may inherit a predisposition to anxiety or stress-related disorders, making them more vulnerable to the effects of trauma. Additionally, abnormalities in brain structure and function, particularly in areas responsible for memory and emotion regulation, can contribute to the development of this condition.
Lack of Social Support
After experiencing trauma, having a strong support system can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition. Conversely, individuals who lack emotional support or face isolation may find it harder to process their experiences. Friends, family, and community networks play a critical role in helping individuals cope with trauma and preventing long-term psychological consequences.
Symptoms of Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
The symptoms of this condition can manifest in various ways, affecting an individual’s thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. These symptoms are typically grouped into four main categories:
Intrusive Memories
One of the hallmark symptoms of this condition is the presence of intrusive memories. These are unwanted and distressing recollections of the traumatic event that intrude on daily life. Common manifestations include:
- Flashbacks, where the individual feels as though they are reliving the trauma
- Recurrent nightmares related to the event
- Intense emotional distress when reminded of the trauma
- Physical reactions, such as sweating or a racing heart, when triggered by reminders
Avoidance Behaviors
Individuals with this condition often go to great lengths to avoid anything that reminds them of the traumatic event. This avoidance can extend to people, places, activities, or even thoughts and feelings associated with the trauma. Examples include:
- Refusing to talk about the event
- Avoiding locations or situations that trigger memories
- Withdrawing from social interactions
- Engaging in distractions to suppress thoughts of the trauma
Negative Changes in Thinking and Mood
This condition can also lead to profound changes in an individual’s thoughts and emotions. These changes often result in feelings of detachment, hopelessness, or emotional numbness. Specific symptoms include:
- Difficulty remembering key details of the traumatic event
- Negative beliefs about oneself or the world
- Feelings of guilt or shame
- Loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities
- Difficulty maintaining close relationships
Changes in Emotional Reactions
Another category of symptoms involves heightened emotional responses and increased arousal. Individuals may feel constantly on edge, as though danger is always present. Common signs include:
- Irritability or angry outbursts
- Hypervigilance, or being overly alert to potential threats
- Difficulty concentrating
- Exaggerated startle response
- Problems with sleep, such as insomnia or restless nights
Treatments for Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
While this condition can be debilitating, there are effective treatments available to help individuals manage their symptoms and regain control of their lives. Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual’s specific needs and may involve a combination of therapies and medications.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, or CBT, is one of the most widely used and effective treatments for this condition. This form of therapy focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with the trauma. Key components of CBT include:
- Exposure therapy, which helps individuals confront and process their traumatic memories in a safe environment
- Cognitive restructuring, which challenges distorted beliefs and helps reframe negative thoughts
- Stress management techniques to reduce anxiety and improve coping skills
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing, often referred to as EMDR, is another evidence-based treatment for this condition. This therapy involves recalling traumatic memories while engaging in guided eye movements or other forms of bilateral stimulation. The goal is to reduce the emotional impact of these memories and help the individual process them in a healthier way.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms of this condition. Antidepressants, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, are commonly used to address issues such as depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. Other medications, such as anti-anxiety drugs or mood stabilizers, may also be recommended based on the individual’s needs.
Group Therapy and Support Networks
Participating in group therapy or support groups can be incredibly beneficial for individuals with this condition. Sharing experiences with others who have faced similar challenges can foster a sense of community and reduce feelings of isolation. Group settings also provide opportunities to learn coping strategies and gain perspective from others’ journeys.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care
In addition to professional treatments, incorporating healthy lifestyle changes can support recovery. These include:
- Regular exercise to reduce stress and improve mood
- Mindfulness practices such as meditation or yoga to promote relaxation
- Maintaining a balanced diet and adequate sleep
- Building a strong support network of friends and family
Final Thoughts
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder is a challenging condition, but with the right support and treatment, individuals can overcome its effects and lead fulfilling lives. By understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and exploring available treatments, we can create a more compassionate and informed approach to addressing this widespread issue.