Anxiety disorders, often referred to as ADs, are among the most common mental health conditions worldwide. These disorders can significantly impact a person’s daily life, affecting their emotional well-being, relationships, and ability to function effectively. Understanding the different types of anxiety disorders, recognizing their symptoms, and exploring treatment options is essential for individuals seeking help and support. This article delves into the various forms of anxiety disorders, outlines their symptoms, and discusses effective treatment strategies.
What Are Anxiety Disorders?
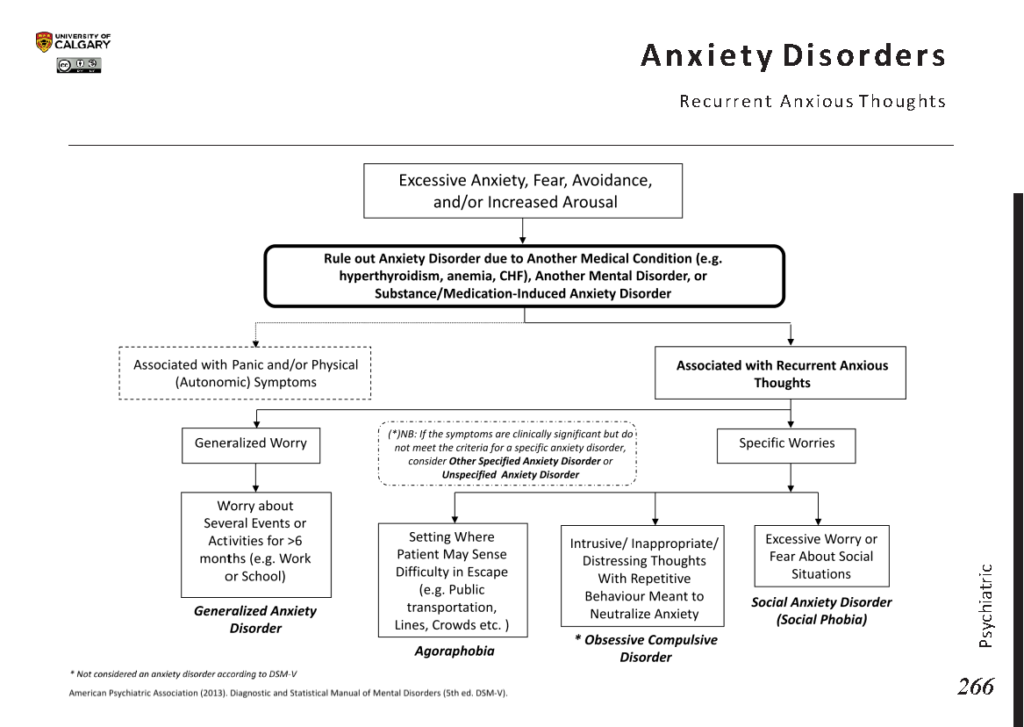
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive fear, worry, or unease. Unlike normal feelings of anxiety that arise in response to specific situations, such as an upcoming exam or job interview, anxiety disorders involve persistent and overwhelming feelings that interfere with daily activities. These feelings may be irrational or disproportionate to the actual threat, making it difficult for individuals to manage their emotions.
While occasional anxiety is a normal part of life, anxiety disorders are chronic and can worsen over time if left untreated. They often coexist with other mental health conditions, such as depression, and can lead to physical symptoms like headaches, fatigue, and digestive issues.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders encompass a wide range of conditions, each with its own unique characteristics. Below are some of the most common types:
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Generalized Anxiety Disorder is marked by persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of life, such as work, health, family, or finances. People with this condition often find it challenging to control their anxiety, even when there is little or no reason for concern. The worry is often accompanied by physical symptoms like muscle tension, restlessness, and difficulty concentrating.
Panic Disorder
Panic Disorder involves recurring panic attacks, which are sudden episodes of intense fear that peak within minutes. During a panic attack, individuals may experience heart palpitations, sweating, trembling, shortness of breath, and a sense of impending doom. These attacks can occur unexpectedly or be triggered by specific situations, leading to a fear of future episodes.
Social Anxiety Disorder
Social Anxiety Disorder is characterized by an intense fear of social situations where one might be judged, embarrassed, or scrutinized by others. People with this condition often avoid social gatherings, public speaking, or situations where they feel they may be the center of attention. This fear can significantly impair their ability to form relationships and engage in everyday activities.
Specific Phobias
Specific Phobias involve an irrational fear of a particular object or situation, such as heights, animals, flying, or enclosed spaces. When exposed to the feared object or situation, individuals may experience extreme anxiety or panic attacks. As a result, they often go to great lengths to avoid the trigger, which can limit their personal and professional lives.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder is marked by unwanted, intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or rituals (compulsions) performed to alleviate anxiety. Common obsessions include fears of contamination, harm, or disorder, while compulsions may involve excessive cleaning, checking, or counting. These behaviors can consume significant amounts of time and interfere with daily functioning.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder occurs after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event, such as combat, natural disasters, or serious accidents. Individuals with this condition may relive the trauma through flashbacks or nightmares, experience heightened alertness, and avoid reminders of the event. These symptoms can persist for months or years, affecting their quality of life.
Separation Anxiety Disorder
Separation Anxiety Disorder is commonly associated with children but can also affect adults. It involves excessive fear or anxiety about being separated from attachment figures, such as parents or partners. This fear can lead to clingy behavior, reluctance to be alone, and physical symptoms like stomachaches or headaches.
Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders
The symptoms of anxiety disorders can vary depending on the type of condition but often include both emotional and physical manifestations. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early intervention and treatment.
Emotional Symptoms
- Excessive worry or fear
- Feeling restless or on edge
- Irritability or mood swings
- Difficulty concentrating or feeling mentally blank
- A sense of impending danger or doom
Physical Symptoms
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Sweating or trembling
- Shortness of breath or hyperventilation
- Muscle tension or aches
- Fatigue or insomnia
- Gastrointestinal issues like nausea or diarrhea
Behavioral Symptoms
- Avoidance of certain situations or places
- Engaging in repetitive behaviors or rituals
- Seeking constant reassurance from others
- Difficulty completing tasks due to perfectionism
Treatment Options for Anxiety Disorders
While anxiety disorders can be debilitating, they are highly treatable with the right interventions. Treatment typically involves a combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes tailored to the individual’s needs.
Therapy
Therapy is one of the most effective ways to address anxiety disorders. Several therapeutic approaches have been proven to help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. Through structured sessions, individuals learn coping strategies, relaxation techniques, and problem-solving skills to manage their symptoms effectively.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure Therapy is particularly useful for treating phobias and post-traumatic stress disorder. It involves gradually exposing individuals to the feared object or situation in a controlled and safe environment, helping them build tolerance and reduce their anxiety over time.
Mindfulness-Based Therapy
Mindfulness-Based Therapy encourages individuals to focus on the present moment without judgment. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and body scans can help reduce stress and promote emotional regulation.
Medication
Medications are often prescribed to complement therapy and provide relief from severe symptoms. The choice of medication depends on the type of anxiety disorder and the individual’s response to treatment.
Antidepressants
Antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, are commonly used to treat anxiety disorders. These medications help regulate brain chemicals that influence mood and anxiety levels.
Anxiolytics
Anxiolytics, or anti-anxiety medications, are designed to provide short-term relief from acute anxiety symptoms. While effective, they are typically prescribed for limited periods due to the risk of dependency.
Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are sometimes used to manage physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heartbeat and trembling. These medications are particularly helpful for individuals with performance anxiety or social anxiety disorder.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to therapy and medication, making certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve symptoms of anxiety disorders.
Regular Exercise
Physical activity has been shown to reduce anxiety by releasing endorphins, improving mood, and promoting better sleep. Activities like walking, jogging, yoga, or dancing can be particularly beneficial.
Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall mental health. Avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods may also help reduce anxiety symptoms.
Sleep Hygiene
Prioritizing good sleep habits is essential for managing anxiety. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment can improve sleep quality and reduce stress.
Stress Management
Learning stress management techniques, such as time management, setting boundaries, and practicing relaxation exercises, can help individuals cope with daily challenges more effectively.
Support Systems and Coping Strategies
Building a strong support system is vital for individuals with anxiety disorders. Friends, family members, and support groups can provide encouragement, understanding, and practical assistance during difficult times. Additionally, developing healthy coping strategies, such as journaling, engaging in hobbies, or seeking spiritual practices, can empower individuals to take control of their mental health.
Support Groups
Joining a support group allows individuals to connect with others who share similar experiences. Sharing stories, exchanging advice, and receiving validation can foster a sense of community and reduce feelings of isolation.
Education and Awareness
Educating oneself about anxiety disorders can demystify the condition and reduce stigma. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower individuals to seek help and advocate for their needs.