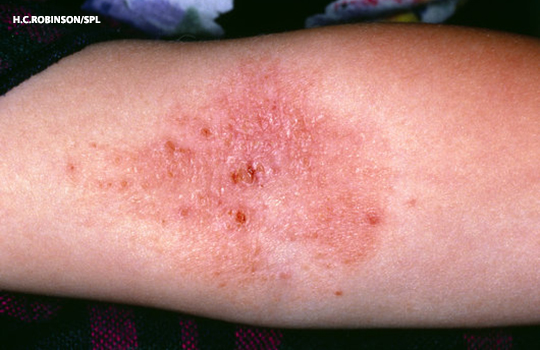
Neurodermatitis, also known as lichen simplex chronicus, is a skin condition characterized by persistent itching and scratching, leading to thickened and irritated patches of skin. This chronic condition can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life due to its uncomfortable symptoms and potential for recurrence. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring treatment options are essential steps in managing this condition effectively.
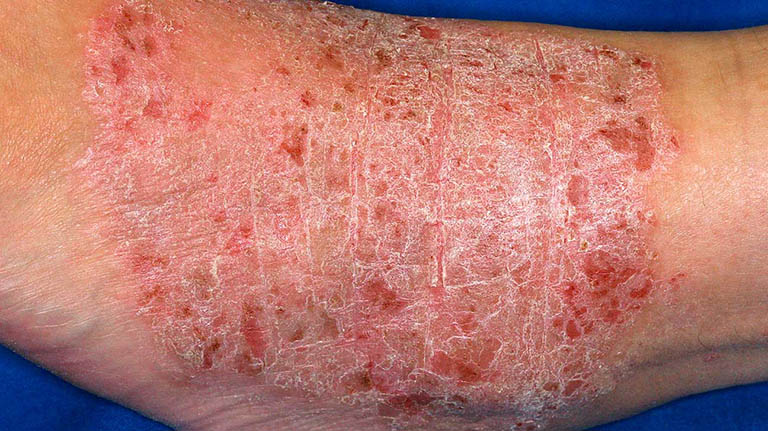
Understanding Neurodermatitis
Neurodermatitis is a type of dermatitis that often begins with a small area of itchy skin. The constant scratching or rubbing leads to a cycle of irritation and thickening of the skin, which only worsens the itch. This condition typically affects adults and is more common in women than men. While the exact cause remains unclear, several factors contribute to its development.
Common Causes of Neurodermatitis
The precise triggers of neurodermatitis vary from person to person, but certain factors are commonly associated with its onset:
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress and anxiety are significant contributors to neurodermatitis. These psychological factors can exacerbate the urge to scratch, creating a vicious cycle.
- Skin Irritants: Exposure to certain fabrics, chemicals, or environmental irritants can trigger itching, especially in individuals with sensitive skin.
- Allergic Reactions: Some people develop neurodermatitis as a result of allergic reactions to substances like soaps, detergents, or perfumes.
- Dry Skin: Individuals with naturally dry skin are more prone to developing neurodermatitis, as dryness increases the likelihood of itching.
- Underlying Skin Conditions: Pre-existing conditions such as eczema or psoriasis can predispose someone to neurodermatitis.
- Nerve Disorders: In some cases, nerve-related issues may lead to abnormal sensations, including persistent itching.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Neurodermatitis manifests through specific symptoms that help differentiate it from other skin conditions. The most common signs include:
- Intense Itching: The hallmark symptom of neurodermatitis is an overwhelming urge to scratch a particular area of the skin. This itching is often worse at night, disrupting sleep patterns.
- Thickened Skin: Prolonged scratching leads to the development of leathery, thickened patches of skin, known as lichenification.
- Redness and Inflammation: The affected areas may appear red and inflamed due to constant irritation.
- Scaly Texture: Over time, the skin may become rough and scaly as a result of repeated scratching.
- Pain or Discomfort: In severe cases, the skin may crack or bleed, causing pain and increasing the risk of infection.
Common Areas Affected by Neurodermatitis
While neurodermatitis can occur anywhere on the body, certain areas are more frequently affected:
- The back of the neck
- Scalp
- Wrists
- Outer arms
- Ankles
- Genital area
Treatment Options for Neurodermatitis
Managing neurodermatitis involves breaking the itch-scratch cycle and addressing the underlying causes. Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual’s specific needs and may include a combination of the following approaches:
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are usually the first line of defense against neurodermatitis. These treatments aim to soothe the skin, reduce inflammation, and alleviate itching:
- Corticosteroid Creams: These creams help reduce inflammation and itching. They are applied directly to the affected areas and should be used under medical supervision to avoid side effects.
- Moisturizers: Regular use of fragrance-free moisturizers helps keep the skin hydrated, reducing dryness and irritation.
- Antihistamine Creams: These creams can provide temporary relief from itching, especially when applied before bedtime.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Non-steroidal topical medications like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus may be prescribed for long-term use to control symptoms without the risks associated with corticosteroids.
Oral Medications
In cases where topical treatments are insufficient, oral medications may be prescribed:
- Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines can help relieve itching, particularly at night, improving sleep quality.
- Anti-anxiety Medications: If stress or anxiety is a contributing factor, medications to manage these conditions may be recommended.
- Antibiotics: If the skin becomes infected due to excessive scratching, antibiotics may be necessary to treat the infection.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can play a crucial role in managing neurodermatitis:
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding irritants or allergens that worsen symptoms is essential. This may include switching to hypoallergenic products or wearing loose-fitting clothing made from natural fibers.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or counseling can help reduce stress levels, thereby minimizing the urge to scratch.
- Healthy Skincare Routine: Maintaining a consistent skincare routine that includes gentle cleansing and regular moisturizing can prevent flare-ups.
- Cool Compresses: Applying cool compresses to the affected areas can provide temporary relief from itching.
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find relief through alternative therapies, although their effectiveness varies:
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique may help reduce stress and alleviate itching in some patients.
- Dietary Changes: Certain foods, such as those high in sugar or processed ingredients, may exacerbate inflammation. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids may be beneficial.
- Hypnotherapy: Hypnosis has been explored as a method to reduce the urge to scratch by altering subconscious behaviors.
Preventing Recurrence of Neurodermatitis
While neurodermatitis can be challenging to manage, taking preventive measures can reduce the likelihood of recurrence:
- Regular Follow-ups: Keeping in touch with a healthcare provider ensures timely adjustments to the treatment plan if needed.
- Early Intervention: Addressing mild symptoms promptly can prevent them from escalating into more severe cases.
- Education and Awareness: Understanding the condition and its triggers empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their symptoms.
Support Systems
Living with neurodermatitis can be emotionally taxing, making support systems invaluable:
- Support Groups: Joining support groups, either online or in person, allows individuals to share experiences and coping strategies.
- Family and Friends: Having a strong support network of loved ones who understand the challenges of the condition can make a significant difference.