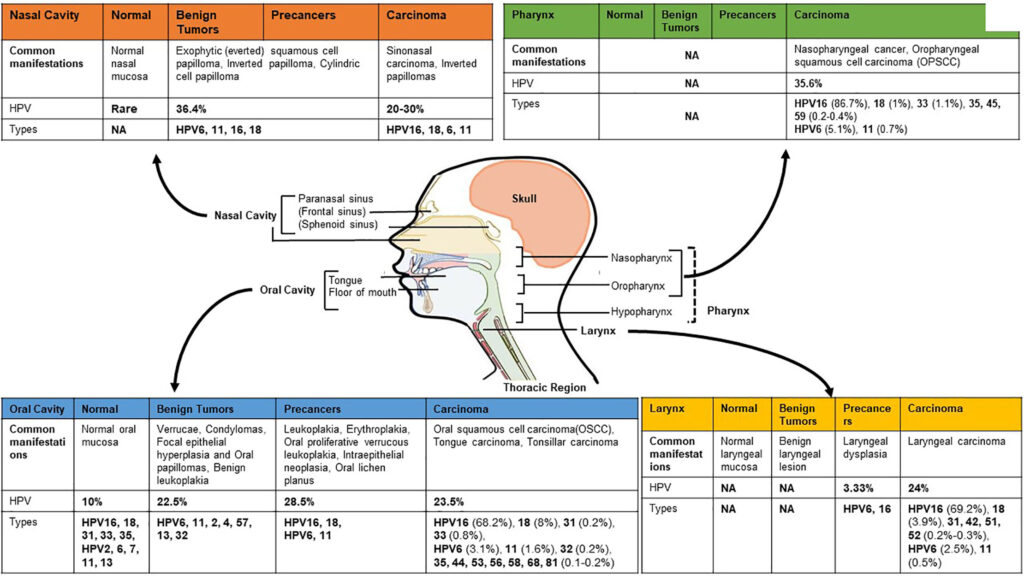
Nasopharyngeal cancer, often abbreviated as NPC, is a rare type of head and neck cancer that originates in the nasopharynx, which is the upper part of the throat behind the nose. This condition has unique characteristics compared to other cancers due to its association with specific risk factors, geographic prevalence, and treatment approaches. In this article, we will explore the overview, causes, symptoms, and available treatments for this disease.
What is Nasopharyngeal Cancer?
Nasopharyngeal cancer begins in the cells lining the nasopharynx, an area located just above the soft palate and below the base of the skull. It is categorized as a squamous cell carcinoma in most cases, meaning it arises from the flat, thin cells that line the surface of the nasopharynx. Unlike many other types of cancer, nasopharyngeal cancer is more common in certain regions of the world, such as Southeast Asia and North Africa, and is relatively rare in Western countries.
Types of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
- Keratinizing Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This type is less common and tends to be associated with tobacco and alcohol use.
- Non-Keratinizing Carcinoma: This is the most common form and is strongly linked to the Epstein-Barr virus.
- Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A rare subtype that shares features with both squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of nasopharyngeal cancer is not fully understood, but several factors have been identified that increase the risk of developing this condition.
Viral Infections
One of the most significant risk factors for nasopharyngeal cancer is infection with the Epstein-Barr virus. This virus is also responsible for infectious mononucleosis and is highly prevalent worldwide. However, not everyone infected with the virus develops cancer, suggesting that other factors play a role in its development.
Genetic Predisposition
Family history can influence the likelihood of developing nasopharyngeal cancer. Certain genetic traits may make individuals more susceptible to the effects of viral infections or environmental factors. Populations with higher rates of the disease, such as those in Southern China, may have inherited genetic vulnerabilities.
Dietary Habits
Consumption of salt-cured fish and meats has been linked to an increased risk of nasopharyngeal cancer. These foods contain nitrosamines, which are chemicals known to damage DNA and promote cancer development. Regions where these dietary habits are common tend to report higher incidences of the disease.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain environmental pollutants, such as formaldehyde and wood dust, may also contribute to the development of nasopharyngeal cancer. Occupational exposure to these substances has been studied as a potential risk factor.
Symptoms of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Identifying nasopharyngeal cancer early can be challenging because its symptoms often mimic those of less serious conditions, such as sinus infections or allergies. However, being aware of the warning signs can lead to earlier diagnosis and better outcomes.
Common Symptoms
- Nasal Congestion: Persistent stuffiness or blockage in one or both nostrils.
- Hearing Problems: Ear pain, ringing in the ears, or hearing loss due to fluid buildup caused by obstruction in the Eustachian tube.
- Nosebleeds: Frequent or unexplained bleeding from the nose.
- Lump in the Neck: Swollen lymph nodes, which may indicate the spread of cancer.
- Headaches: Persistent headaches that do not respond to over-the-counter medications.
- Facial Numbness: Loss of sensation or tingling in parts of the face.
Advanced Symptoms
In later stages, the cancer may spread to nearby structures or distant organs, leading to additional symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, vision changes, or bone pain. If any of these symptoms persist, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Diagnosis of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Diagnosing nasopharyngeal cancer typically involves a combination of physical examinations, imaging tests, and laboratory analyses.
Physical Examination
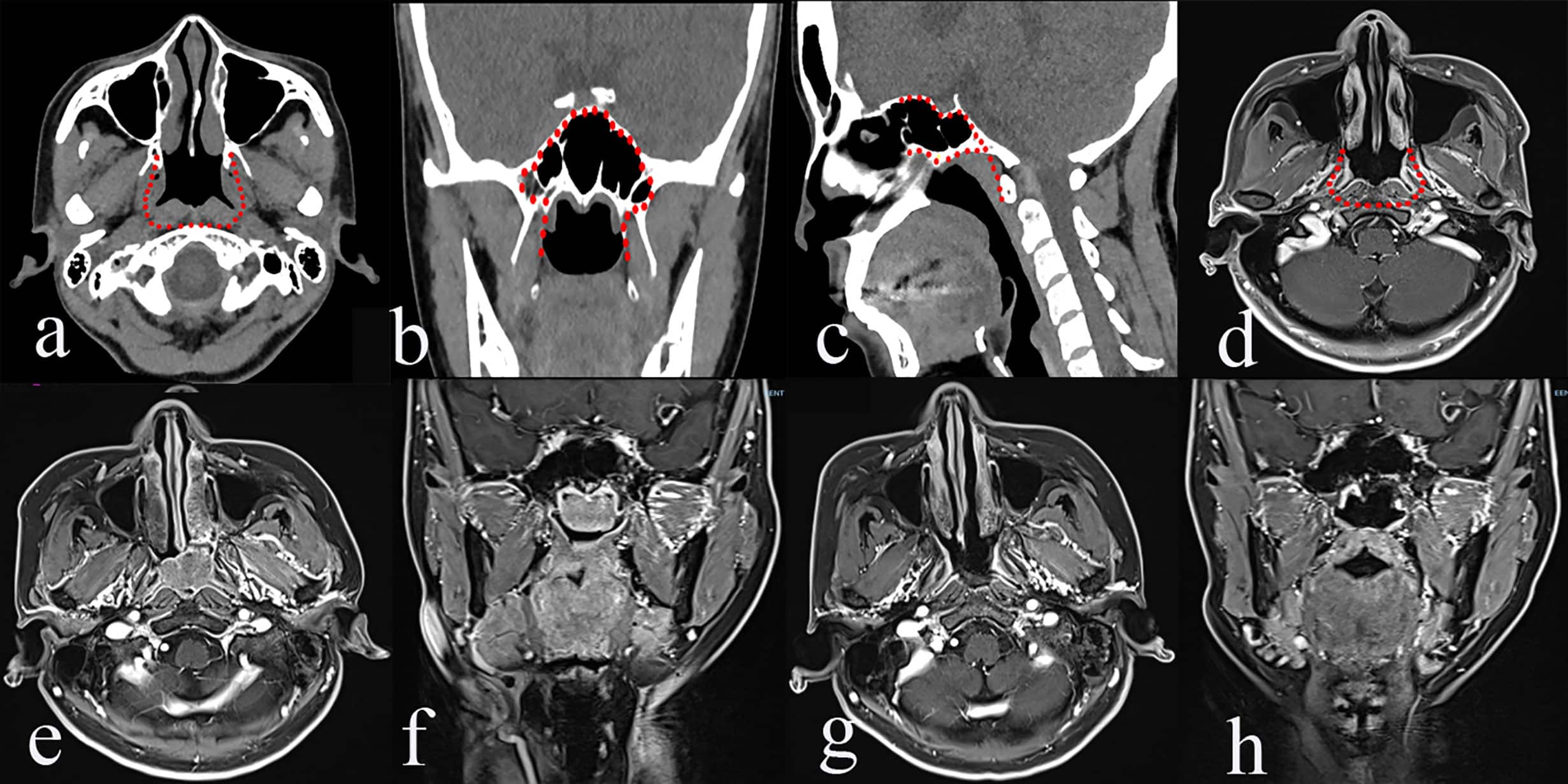
A doctor will perform a thorough examination of the nasal passages, throat, and neck to check for abnormalities. They may use specialized tools, such as an endoscope, to get a closer look at the nasopharynx.
Imaging Tests
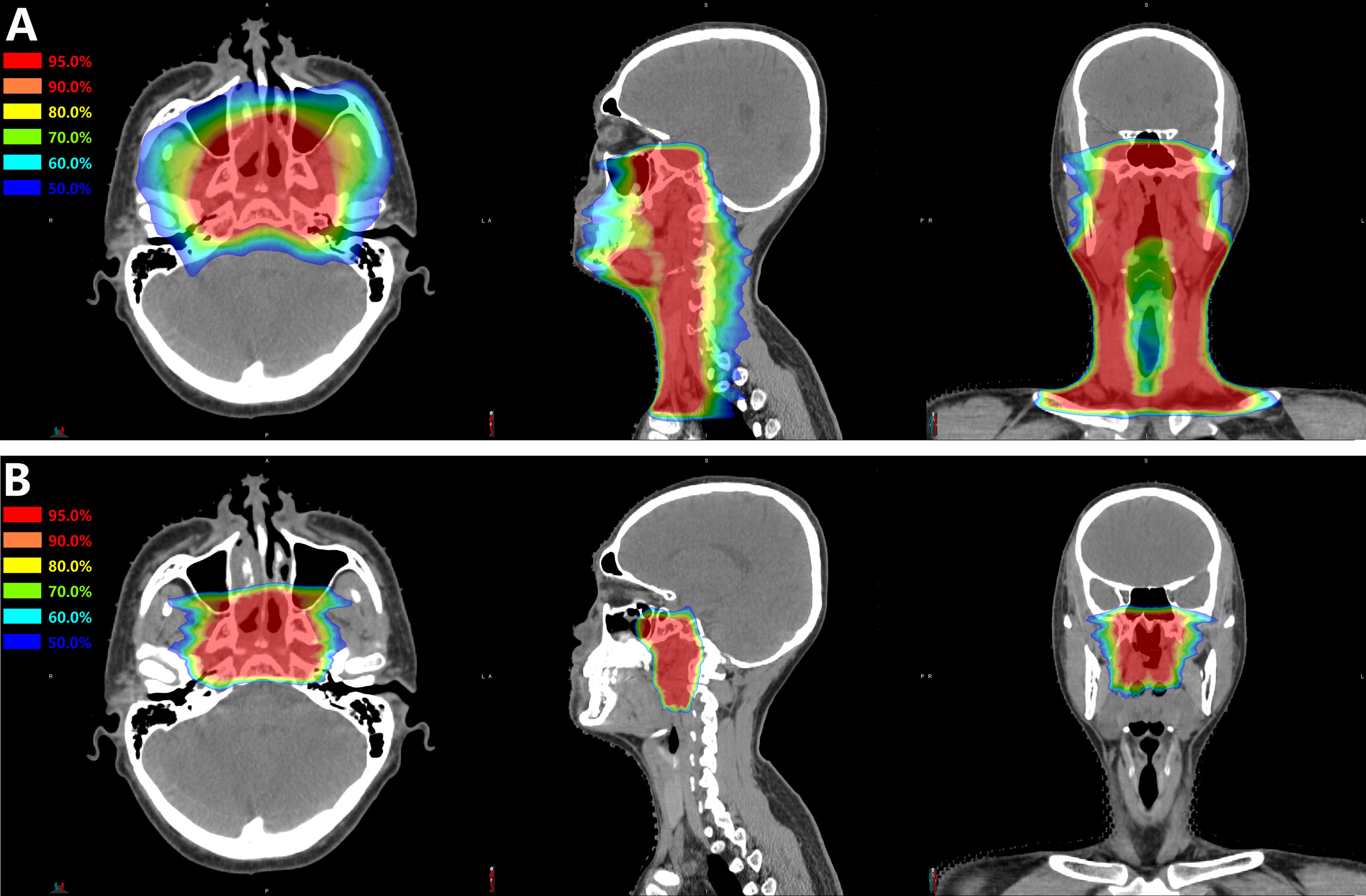
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of soft tissues and helps determine the extent of the tumor.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Offers cross-sectional views of the body and identifies whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes or other areas.
- PET Scan: Helps detect cancerous activity throughout the body by highlighting areas with high metabolic rates.
Biopsy
A biopsy is the definitive method for diagnosing nasopharyngeal cancer. During this procedure, a small sample of tissue is removed from the suspected area and examined under a microscope for cancerous cells.
Treatment Options for Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer depends on several factors, including the stage of the disease, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences. The primary treatment modalities include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and surgery.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is the cornerstone of treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer. High-energy beams are used to target and destroy cancer cells while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. For early-stage cases, radiation alone may be sufficient to achieve remission.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. It is often combined with radiation therapy, especially for advanced stages of the disease. Chemotherapy can also be administered before or after radiation to enhance effectiveness.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is less commonly used for nasopharyngeal cancer due to the location of the tumor and the complexity of the surrounding anatomy. However, it may be considered in cases where the cancer recurs or does not respond to other treatments. Procedures may involve removing lymph nodes or reconstructing affected areas.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapies are designed to attack specific molecules involved in cancer growth and progression. These treatments are generally reserved for patients with advanced or recurrent disease who have exhausted other options.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy harnesses the power of the immune system to fight cancer. While still under investigation for nasopharyngeal cancer, some immunotherapeutic agents have shown promise in clinical trials.
Living with Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Managing life with nasopharyngeal cancer requires a multidisciplinary approach involving medical professionals, caregivers, and support networks. Patients may experience side effects from treatment, such as fatigue, nausea, or difficulty swallowing, which can impact their quality of life. Support groups and counseling services can provide emotional and practical assistance during this challenging time.
Follow-Up Care
Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor recovery and detect any recurrence of the disease. These visits may include physical exams, imaging tests, and blood work to ensure ongoing health and well-being.