Nasal polyps, often abbreviated as NP, are soft, noncancerous growths that develop on the lining of the nasal passages or sinuses. These growths can vary in size and may cause a range of symptoms depending on their location and severity. While they are not life-threatening, nasal polyps can significantly impact a person’s quality of life by causing breathing difficulties, recurring infections, and other complications. This article provides an in-depth look at nasal polyps, including their causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
What Are Nasal Polyps?
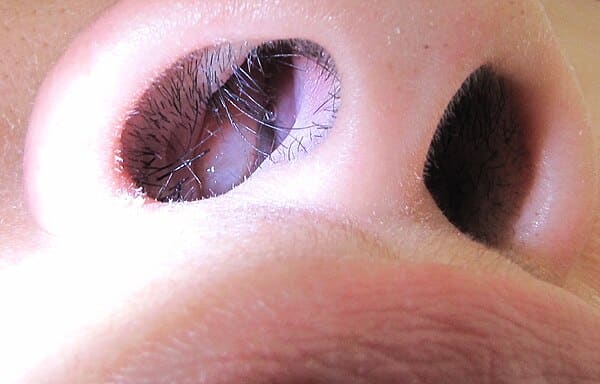
Nasal polyps are teardrop-shaped growths that form in the nasal passages or sinuses. They are typically soft and painless, resembling small clusters of grapes hanging from the lining of the nasal cavity. Although they are benign, these growths can obstruct airflow and lead to chronic nasal congestion, reduced sense of smell, and other related issues.
Nasal polyps can occur in anyone, but they are more common in adults than in children. People with certain medical conditions, such as asthma or allergies, are at a higher risk of developing them. Understanding what nasal polyps are is the first step toward recognizing their symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment.
Causes of Nasal Polyps
The exact cause of nasal polyps remains unclear, but researchers believe they result from chronic inflammation in the nasal passages or sinuses. Several factors may contribute to this inflammation and increase the likelihood of polyp formation:
Chronic Inflammation
- Prolonged Irritation: Continuous irritation of the nasal lining due to allergies, infections, or environmental irritants can lead to swelling and eventually the development of polyps.
- Immune System Response: An overactive immune response to certain triggers may cause persistent inflammation, creating an environment conducive to polyp growth.
Underlying Medical Conditions
- Asthma: People with asthma are more likely to develop nasal polyps, possibly due to shared inflammatory pathways between the respiratory system and nasal passages.
- Allergic Rhinitis: Also known as hay fever, allergic rhinitis can cause chronic nasal inflammation, increasing the risk of polyps.
- Cystic Fibrosis: This genetic condition affects the production of mucus, leading to thick, sticky secretions that can promote polyp formation.
Infections
- Recurrent Sinus Infections: Frequent sinus infections can damage the nasal lining and trigger the growth of polyps.
- Fungal Infections: Certain fungal infections in the nasal passages may also contribute to polyp development.
Symptoms of Nasal Polyps
The symptoms of nasal polyps can vary depending on their size and location. Some people may experience mild discomfort, while others may face significant challenges in their daily lives. Common symptoms include:
Nasal Congestion
One of the most noticeable signs of nasal polyps is a feeling of stuffiness or blockage in the nose. This occurs because the polyps obstruct the nasal passages, making it difficult for air to flow freely.
Reduced Sense of Smell
Many individuals with nasal polyps report a diminished ability to detect odors. This loss of smell, known as anosmia, can affect taste perception and reduce the enjoyment of food.
Postnasal Drip
Excess mucus production caused by nasal polyps can lead to postnasal drip, where mucus drips down the back of the throat. This can result in a persistent cough or sore throat.
Facial Pain or Pressure
Large polyps or multiple growths can exert pressure on the sinuses, leading to facial pain, headaches, or a feeling of fullness in the face.
Frequent Sinus Infections
Because nasal polyps interfere with normal drainage of the sinuses, they can increase the risk of recurrent sinus infections, which may require ongoing treatment.
Sleep Disturbances
Nasal congestion caused by polyps can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to snoring, sleep apnea, or general restlessness during the night.
Diagnosis of Nasal Polyps
If you suspect you have nasal polyps, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. The diagnostic process typically involves:
Physical Examination
A doctor will examine your nasal passages using a lighted instrument called a nasal speculum. In some cases, they may use a specialized tool called an endoscope to get a closer look at the nasal cavity and sinuses.
Imaging Tests
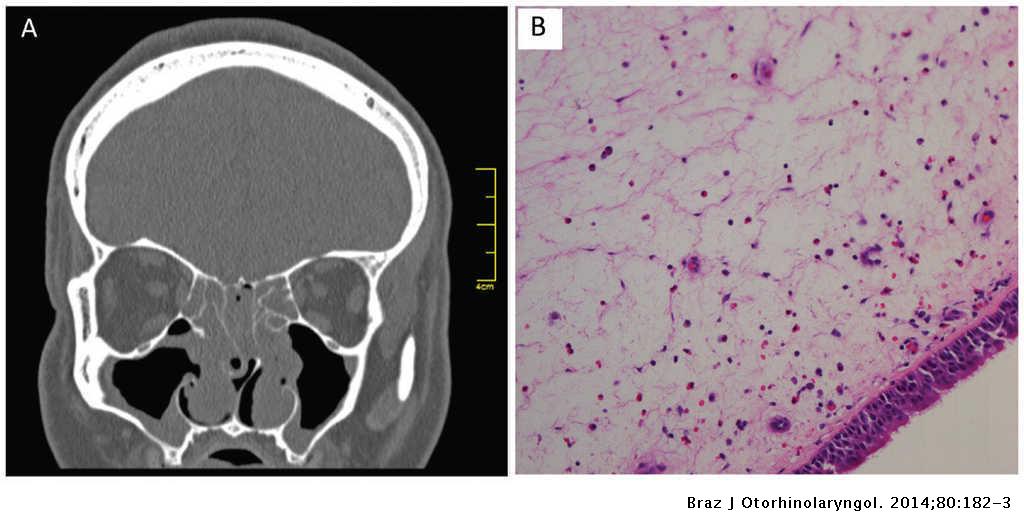
To confirm the presence of nasal polyps and assess their size and location, imaging tests such as computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be recommended.
Allergy Testing
Since allergies can contribute to nasal polyp formation, allergy testing may be performed to identify potential triggers and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Options for Nasal Polyps
Treatment for nasal polyps focuses on reducing inflammation, alleviating symptoms, and preventing recurrence. Depending on the severity of the condition, treatment options may include medications, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery.
Medications
Several types of medications can help manage nasal polyps:
- Corticosteroid Sprays: These nasal sprays reduce inflammation and shrink polyps. They are often used as a first-line treatment.
- Oral Corticosteroids: For more severe cases, oral corticosteroids may be prescribed to quickly reduce inflammation. However, long-term use is generally avoided due to potential side effects.
- Antihistamines: If allergies are contributing to polyp formation, antihistamines can help control symptoms.
- Antibiotics: If a bacterial infection is present, antibiotics may be necessary to clear the infection before addressing the polyps.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For individuals who do not respond to medications, minimally invasive procedures may be considered:
- Nasal Polypectomy: This outpatient procedure involves removing polyps using special tools inserted through the nostrils.
- Balloon Sinuplasty: A balloon catheter is used to widen the sinus openings, improving drainage and reducing the likelihood of polyp recurrence.
Surgical Interventions
In cases where polyps are large or recurrent, surgery may be required:
- Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: This procedure uses an endoscope to remove polyps and improve sinus drainage. It is typically performed under general anesthesia and has a high success rate.
- Caldwell-Luc Procedure: Reserved for complex cases, this surgery involves accessing the sinuses through the upper jaw to remove polyps and address underlying structural issues.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can complement the management of nasal polyps:
- Humidifiers: Using a humidifier at home can keep the nasal passages moist, reducing irritation and promoting healing.
- Saltwater Rinses: Regularly rinsing the nasal passages with a saline solution can help clear mucus and reduce inflammation.
- Avoiding Irritants: Staying away from smoke, strong odors, and other environmental irritants can prevent further inflammation.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can support overall immune health and reduce inflammation.
Preventing Recurrence of Nasal Polyps
While it may not always be possible to prevent nasal polyps entirely, certain strategies can help minimize the risk of recurrence:
- Consistent Medication Use: Adhering to prescribed medication regimens, especially corticosteroid sprays, can keep inflammation under control.
- Regular Follow-Ups: Routine visits to a healthcare provider allow for early detection and management of any new growths.
- Allergy Management: Effectively managing allergies through avoidance of triggers and appropriate treatment can reduce the likelihood of polyp formation.