Myasthenia Gravis, often abbreviated as MG, is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the communication between nerves and muscles. This condition leads to muscle weakness and fatigue, significantly impacting daily life for those who suffer from it. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of this condition, exploring its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What Is Myasthenia Gravis?
Myasthenia Gravis is a neuromuscular disorder characterized by the weakening of voluntary muscles. The name itself comes from Greek and Latin origins, meaning “grave muscle weakness.” This condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, specifically targeting the connection points between nerves and muscles. These connection points are known as neuromuscular junctions.
How Does It Affect the Body?
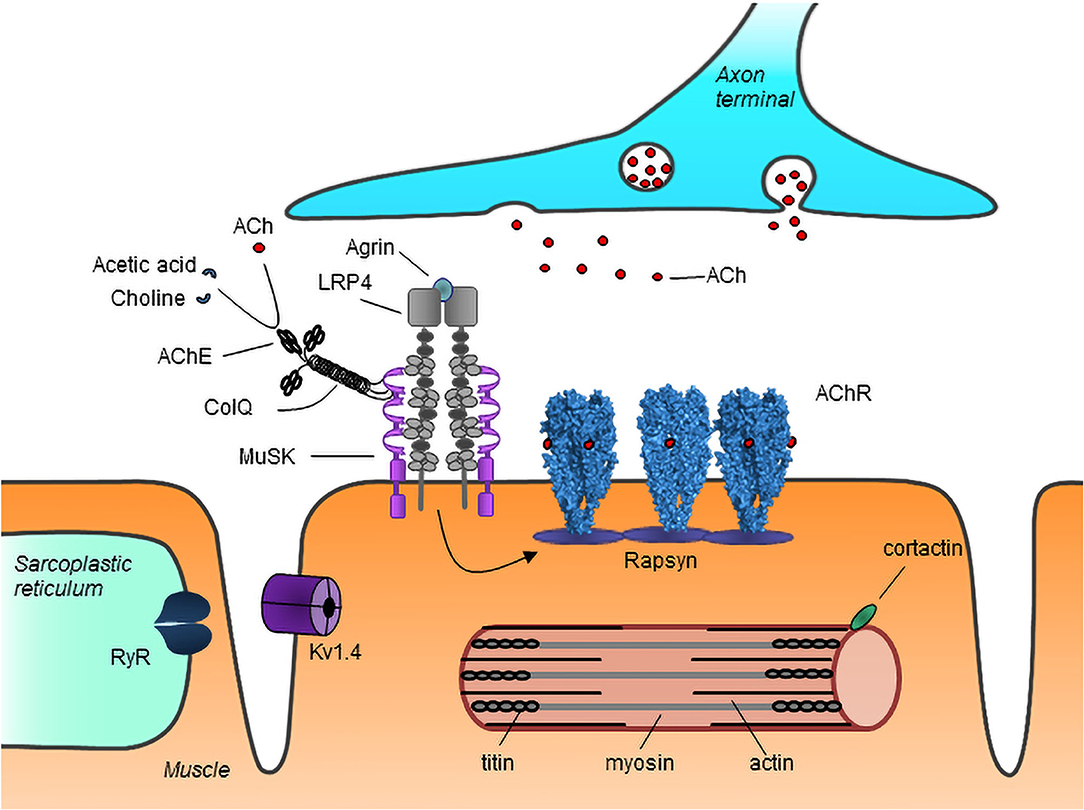
In a healthy individual, signals travel from the brain through the nervous system to the muscles, enabling movement. At the neuromuscular junction, these signals are transmitted via neurotransmitters, primarily acetylcholine. Acetylcholine binds to receptors on the muscle surface, triggering muscle contractions. However, in individuals with this condition, the immune system produces antibodies that block or destroy these receptors, impairing communication and causing muscle weakness.
Symptoms of Myasthenia Gravis
The symptoms of this condition can vary widely among individuals, but they generally involve muscle weakness that worsens with activity and improves with rest. Below are some common symptoms:
- Drooping Eyelids: One of the earliest signs is ptosis, or drooping of one or both eyelids.
- Double Vision: Many individuals experience diplopia, or double vision, due to weakened eye muscles.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Weakness in throat muscles can make swallowing challenging, leading to choking or aspiration.
- Slurred Speech: Muscle weakness in the face and throat can cause speech difficulties.
- Fatigue: Generalized muscle fatigue is a hallmark symptom, often worsening as the day progresses.
- Weakened Limbs: Arms and legs may feel weak, making activities like lifting objects or climbing stairs difficult.
Factors That Worsen Symptoms
Certain factors can exacerbate the symptoms of this condition, including:
- Stress
- Illness or infection
- Extreme temperatures
- Physical exertion
- Medications such as beta-blockers or certain antibiotics
Causes of Myasthenia Gravis
The exact cause of this condition remains unknown, but researchers believe it results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Here’s a closer look at what might contribute to its development:
Autoimmune Response
In individuals with this condition, the immune system produces antibodies that target acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction. These antibodies interfere with the normal functioning of the receptors, preventing muscles from contracting effectively. In some cases, the immune system may also attack other components of the neuromuscular junction, further complicating the condition.
Thymus Gland Abnormalities
The thymus gland, located in the chest, plays a crucial role in the development of the immune system. In many individuals with this condition, abnormalities in the thymus gland have been observed. Some people develop tumors in the thymus, known as thymomas, which may contribute to the production of harmful antibodies. Surgical removal of the thymus, called thymectomy, is sometimes recommended as a treatment option.
Genetic Predisposition
While this condition is not directly inherited, there may be a genetic predisposition that increases the likelihood of developing it. Certain genes related to immune system function have been linked to an increased risk. Family history of autoimmune disorders may also play a role.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors such as infections, stress, or exposure to certain chemicals may trigger the onset of symptoms in genetically susceptible individuals. For example, viral infections have been associated with the initial appearance of symptoms in some cases.
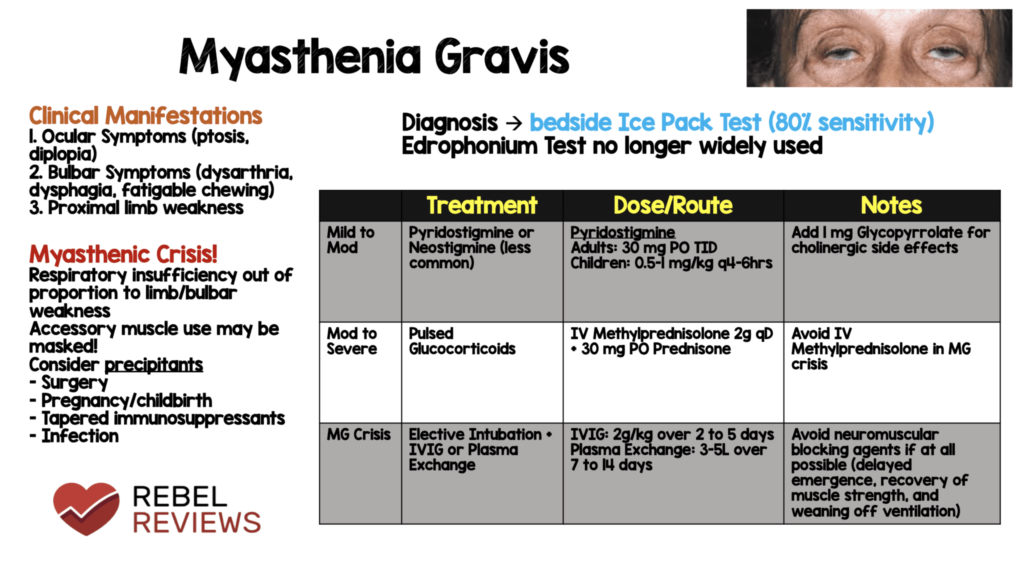
Diagnosing Myasthenia Gravis
Diagnosing this condition can be challenging because its symptoms mimic those of other neurological and muscular disorders. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is essential. Below are some common diagnostic methods:
Physical Examination
A doctor will assess muscle strength and reflexes during a physical examination. They may ask the patient to perform specific tasks, such as holding their arms outstretched or looking upward for an extended period, to observe muscle fatigue.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can detect the presence of antibodies against acetylcholine receptors or other components of the neuromuscular junction. While not all patients have detectable antibodies, their presence strongly supports a diagnosis of this condition.
Electromyography (EMG)
This test measures the electrical activity of muscles and nerves. During an EMG, small electrodes are inserted into the muscles to record their response to nerve stimulation. In individuals with this condition, the muscles may show abnormal responses, such as rapid fatigue.
Edrophonium Test
The edrophonium test involves injecting a drug called edrophonium chloride, which temporarily enhances the action of acetylcholine. If muscle strength improves shortly after the injection, it suggests the presence of this condition.
Imaging Studies
A CT scan or MRI may be performed to examine the thymus gland for abnormalities or tumors. These imaging studies help guide treatment decisions, particularly if thymectomy is being considered.
Treatment Options for Myasthenia Gravis
While there is no cure for this condition, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment plans are tailored to the individual based on the severity of symptoms and their impact on daily activities.
Medications
Several medications are commonly used to treat this condition:
- Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: Drugs like pyridostigmine enhance the availability of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction, improving muscle strength.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications such as prednisone or azathioprine suppress the immune system to reduce antibody production.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Rituximab and eculizumab are newer therapies that target specific components of the immune system.
Thymectomy
Surgical removal of the thymus gland is recommended for some patients, especially those with thymomas. Thymectomy has been shown to improve symptoms and, in some cases, lead to remission.
Plasmapheresis and Intravenous Immunoglobulin
For severe or rapidly worsening symptoms, procedures like plasmapheresis or intravenous immunoglobulin therapy may be used. Plasmapheresis removes harmful antibodies from the blood, while immunoglobulin therapy introduces healthy antibodies to modulate the immune response.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms:
- Avoiding excessive physical exertion
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques
- Eating soft foods to ease swallowing difficulties
- Using assistive devices for mobility if needed
Living with Myasthenia Gravis
Living with this condition requires ongoing management and adaptation. Patients often work closely with a team of healthcare providers, including neurologists, physical therapists, and dietitians, to address their unique needs. Support groups and counseling can also provide emotional support and practical advice for coping with the challenges of the condition.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor disease progression and adjust treatment plans as needed. Patients should report any new or worsening symptoms promptly to their healthcare provider.
Pregnancy and Myasthenia Gravis
Women with this condition can have successful pregnancies, but careful planning and monitoring are essential. Some medications may need to be adjusted during pregnancy to ensure the safety of both mother and baby.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand the underlying mechanisms of this condition and develop more effective treatments. Advances in immunology and genetics hold promise for personalized therapies that target the root causes of the disorder.