Traveling across time zones can be an exciting experience, but it often comes with a downside known as jet lag. Jet lag, or desynchronosis, occurs when your body’s internal clock is disrupted due to rapid travel across multiple time zones. This condition can leave you feeling fatigued, disoriented, and unable to perform at your best. In this article, we will explore the causes of jet lag, its common symptoms, and effective strategies to cope with and minimize its impact.
What Causes Jet Lag?
Jet lag arises from the mismatch between your body’s natural circadian rhythm and the external environment of your destination. The circadian rhythm is your body’s internal clock, which regulates sleep-wake cycles, hormone production, digestion, and other essential functions. When you travel across time zones, your body struggles to adjust to the new schedule, leading to jet lag.
Role of Light Exposure
One of the primary factors influencing your circadian rhythm is light exposure. Your body relies on natural light cues to determine when to feel awake and when to wind down for sleep. When you travel to a different time zone, the timing of daylight and darkness may not align with your body’s expectations, causing confusion in your internal clock.
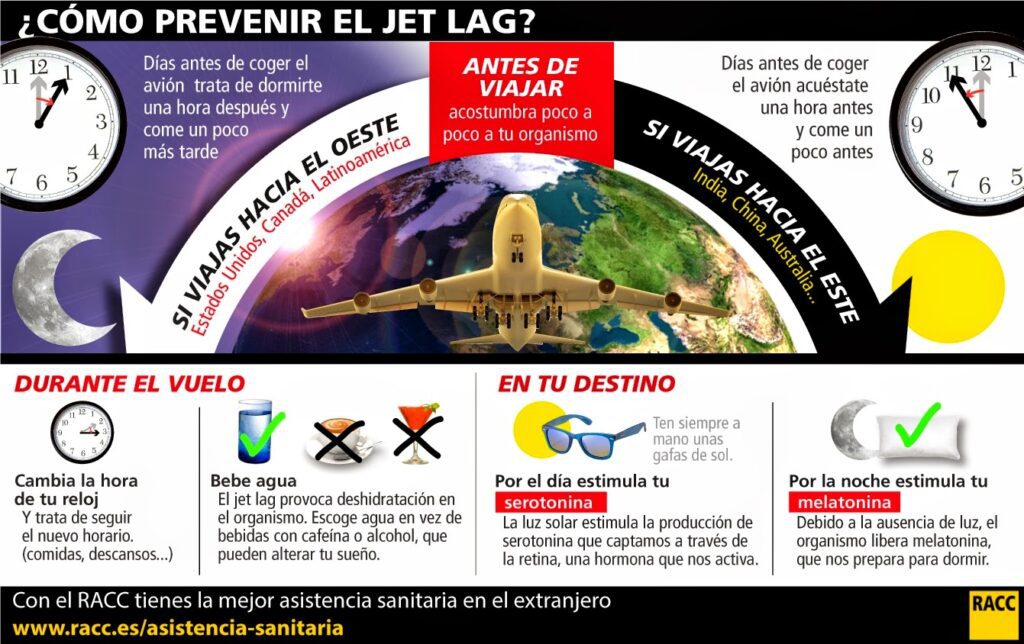
Direction of Travel
- Eastward Travel: Traveling east typically causes more severe jet lag because you are “losing” time and need to adjust your schedule earlier than usual.
- Westward Travel: Traveling west is generally easier to adapt to since you are “gaining” time and can stay up later without much difficulty.
Number of Time Zones Crossed
The greater the number of time zones you cross, the more pronounced the effects of jet lag tend to be. For example, traveling from New York to London involves crossing five time zones, while a trip from Los Angeles to Tokyo crosses as many as sixteen. The larger the time difference, the harder it is for your body to synchronize with the new environment.
Symptoms of Jet Lag
Jet lag manifests through a variety of physical and mental symptoms. These symptoms can vary in intensity depending on factors such as the number of time zones crossed, your age, and your overall health. Below are some of the most common signs of jet lag.
Fatigue and Sleep Disturbances
One of the hallmark symptoms of jet lag is extreme tiredness during the day and difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep at night. This disruption in sleep patterns can lead to insomnia or excessive daytime drowsiness, making it challenging to maintain productivity and focus.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Changes in meal times and eating habits can upset your digestive system, resulting in symptoms like indigestion, constipation, diarrhea, or a general feeling of discomfort. Your appetite may also fluctuate, leading to overeating or loss of interest in food.
Mood Changes
Jet lag can affect your emotional well-being, causing irritability, anxiety, or feelings of depression. These mood swings are often linked to sleep deprivation and hormonal imbalances caused by the disruption of your circadian rhythm.
Cognitive Impairment
Difficulty concentrating, memory lapses, and reduced mental clarity are common cognitive effects of jet lag. These issues can impair decision-making abilities and make even simple tasks seem overwhelming.
Physical Symptoms
In addition to fatigue, jet lag can cause headaches, muscle soreness, and a general sense of malaise. Some people may also experience mild nausea or dizziness as their bodies struggle to adapt to the new time zone.
Coping Strategies for Jet Lag
While jet lag cannot be completely avoided, there are several strategies you can employ to minimize its effects and recover more quickly. By preparing ahead of time and adopting healthy habits during and after your trip, you can ease the transition to a new time zone.
Adjust Your Schedule Before Traveling
If possible, begin shifting your sleep and meal times a few days before your trip to align with the destination’s time zone. Gradually adjusting your routine can help reduce the shock to your system once you arrive.
Tips for Shifting Your Routine:
- Go to bed and wake up one hour earlier or later each day, depending on whether you’re traveling east or west.
- Change your meal times incrementally to match the schedule of your destination.
- Expose yourself to bright light or dim lighting at appropriate times to simulate the conditions of your destination.
Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can exacerbate the symptoms of jet lag, so it’s crucial to drink plenty of water before, during, and after your flight. Avoid alcohol and caffeine, as these substances can interfere with hydration levels and disrupt sleep patterns.
Optimize Light Exposure
Light is one of the most powerful tools for resetting your circadian rhythm. Upon arrival, try to expose yourself to natural sunlight during the day to signal to your body that it’s time to be awake. Conversely, avoid bright screens and artificial light in the evening to promote better sleep.
Using Light Therapy:
For travelers who frequently cross multiple time zones, portable light therapy devices can be helpful. These devices mimic natural sunlight and can be used to regulate your body’s response to changing environments.
Take Strategic Naps
Short naps can provide temporary relief from fatigue, but they should be timed carefully to avoid interfering with nighttime sleep. Limit naps to 20-30 minutes and avoid napping late in the afternoon or evening.
Exercise and Stretch
Physical activity can boost energy levels and improve mood, helping to counteract the sluggishness associated with jet lag. Simple exercises like walking, stretching, or yoga can be particularly beneficial during long flights to prevent stiffness and promote circulation.
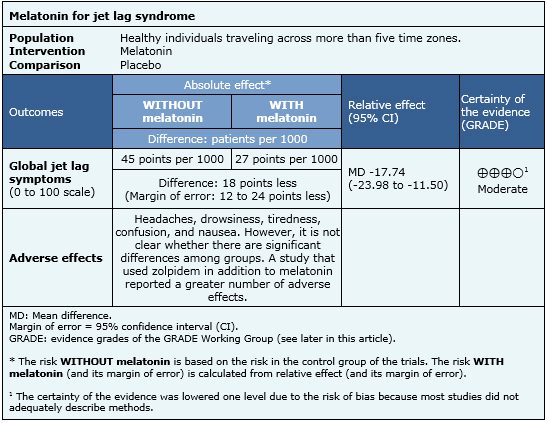
Use Melatonin Supplements
Melatonin is a hormone naturally produced by the body to regulate sleep. Taking melatonin supplements at the appropriate time can help reset your internal clock and facilitate better sleep. However, consult with a healthcare professional before using melatonin, especially if you have underlying medical conditions or take other medications.
Eat Light and Healthy Meals
Heavy meals can weigh you down and worsen feelings of lethargy. Opt for light, nutritious foods that are easy to digest, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Eating smaller portions more frequently can also help stabilize energy levels throughout the day.
Practice Relaxation Techniques
Stress and anxiety can intensify the symptoms of jet lag. Incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or mindfulness exercises can help calm your mind and improve overall well-being.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While jet lag is usually temporary and resolves within a few days, persistent symptoms may indicate an underlying issue. If you experience prolonged fatigue, chronic insomnia, or significant mood disturbances, it may be wise to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Potential Underlying Conditions
In rare cases, frequent jet lag could contribute to the development of sleep disorders or exacerbate existing health problems. A healthcare professional can assess your situation and recommend personalized interventions to address any concerns.